EPRS is a critical mTORC1-S6K1 effector that influences adiposity in mice
- PMID: 28178239
- PMCID: PMC5480610
- DOI: 10.1038/nature21380
EPRS is a critical mTORC1-S6K1 effector that influences adiposity in mice
Abstract
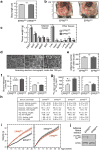
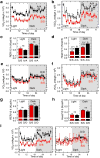
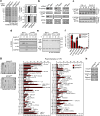
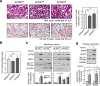
Metabolic pathways that contribute to adiposity and ageing are activated by the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) and p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) axis. However, known mTORC1-S6K1 targets do not account for observed loss-of-function phenotypes, suggesting that there are additional downstream effectors of this pathway. Here we identify glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase (EPRS) as an mTORC1-S6K1 target that contributes to adiposity and ageing. Phosphorylation of EPRS at Ser999 by mTORC1-S6K1 induces its release from the aminoacyl tRNA multisynthetase complex, which is required for execution of noncanonical functions of EPRS beyond protein synthesis. To investigate the physiological function of EPRS phosphorylation, we generated Eprs knock-in mice bearing phospho-deficient Ser999-to-Ala (S999A) and phospho-mimetic (S999D) mutations. Homozygous S999A mice exhibited low body weight, reduced adipose tissue mass, and increased lifespan, similar to S6K1-deficient mice and mice with adipocyte-specific deficiency of raptor, an mTORC1 constituent. Substitution of the EprsS999D allele in S6K1-deficient mice normalized body mass and adiposity, indicating that EPRS phosphorylation mediates S6K1-dependent metabolic responses. In adipocytes, insulin stimulated S6K1-dependent EPRS phosphorylation and release from the multisynthetase complex. Interaction screening revealed that phospho-EPRS binds SLC27A1 (that is, fatty acid transport protein 1, FATP1), inducing its translocation to the plasma membrane and long-chain fatty acid uptake. Thus, EPRS and FATP1 are terminal mTORC1-S6K1 axis effectors that are critical for metabolic phenotypes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures









Comment in
-
Physiology: An atypical switch for metabolism and ageing.Nature. 2017 Feb 16;542(7641):299-300. doi: 10.1038/nature21500. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28178230 Free PMC article.
-
Papers of note in Nature542 (7641).Sci Signal. 2017 Feb 21;10(467):eaam9984. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aam9984. Sci Signal. 2017. PMID: 28223419
-
Unexpected metabolic function of a tRNA synthetase.Cell Cycle. 2017;16(23):2239-2240. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1324127. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Cell Cycle. 2017. PMID: 28777042 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Magnuson B, Ekim B, Fingar DC. Regulation and function of ribosomal protein S6 kinase (S6K) within mTOR signalling networks. Biochem J. 2012;441:1–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

