μCT of ex-vivo stained mouse hearts and embryos enables a precise match between 3D virtual histology, classical histology and immunochemistry
- PMID: 28178293
- PMCID: PMC5298245
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170597
μCT of ex-vivo stained mouse hearts and embryos enables a precise match between 3D virtual histology, classical histology and immunochemistry
Abstract
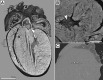
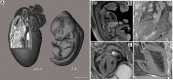
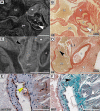
The small size of the adult and developing mouse heart poses a great challenge for imaging in preclinical research. The aim of the study was to establish a phosphotungstic acid (PTA) ex-vivo staining approach that efficiently enhances the x-ray attenuation of soft-tissue to allow high resolution 3D visualization of mouse hearts by synchrotron radiation based μCT (SRμCT) and classical μCT. We demonstrate that SRμCT of PTA stained mouse hearts ex-vivo allows imaging of the cardiac atrium, ventricles, myocardium especially its fibre structure and vessel walls in great detail and furthermore enables the depiction of growth and anatomical changes during distinct developmental stages of hearts in mouse embryos. Our x-ray based virtual histology approach is not limited to SRμCT as it does not require monochromatic and/or coherent x-ray sources and even more importantly can be combined with conventional histological procedures. Furthermore, it permits volumetric measurements as we show for the assessment of the plaque volumes in the aortic valve region of mice from an ApoE-/- mouse model. Subsequent, Masson-Goldner trichrome staining of paraffin sections of PTA stained samples revealed intact collagen and muscle fibres and positive staining of CD31 on endothelial cells by immunohistochemistry illustrates that our approach does not prevent immunochemistry analysis. The feasibility to scan hearts already embedded in paraffin ensured a 100% correlation between virtual cut sections of the CT data sets and histological heart sections of the same sample and may allow in future guiding the cutting process to specific regions of interest. In summary, since our CT based virtual histology approach is a powerful tool for the 3D depiction of morphological alterations in hearts and embryos in high resolution and can be combined with classical histological analysis it may be used in preclinical research to unravel structural alterations of various heart diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Bartels M, Krenkel M, Haber J, Wilke RN, Salditt T. X-Ray Holographic Imaging of Hydrated Biological Cells in Solution. Phys Rev Lett. 2015;114. - PubMed
-
- Keggin JF. Structure of the Molecule of i2-Phosphotungstic. Nature. 1933;131: 908–909.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

