MNK Controls mTORC1:Substrate Association through Regulation of TELO2 Binding with mTORC1
- PMID: 28178522
- PMCID: PMC5321627
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.01.023
MNK Controls mTORC1:Substrate Association through Regulation of TELO2 Binding with mTORC1
Abstract
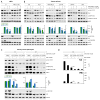
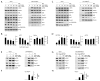
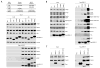
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) integrates numerous stimuli and coordinates the adaptive response of many cellular processes. To accomplish this, mTOR associates with distinct co-factors that determine its signaling output. While many of these co-factors are known, in many cases their function and regulation remain opaque. The MAPK-interacting kinase (MNK) contributes to rapamycin resistance in cancer cells. Here, we demonstrate that MNK sustains mTORC1 activity following rapamycin treatment and contributes to mTORC1 signaling following T cell activation and growth stimuli in cancer cells. We determine that MNK engages with mTORC1, promotes mTORC1 association with the phosphatidyl inositol 3' kinase-related kinase (PIKK) stabilizer, TELO2, and facilitates mTORC1:substrate binding. Moreover, our data suggest that DEPTOR, the endogenous inhibitor of mTOR, opposes mTORC1:substrate association by preventing TELO2:mTORC1 binding. Thus, MNK orchestrates counterbalancing forces that regulate mTORC1 enzymatic activity.
Keywords: DDB1; DEPTOR; MNK; PIKK; S6 kinase; T cell; TELO2; mTOR; rapamycin; raptor.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Adesso L, Calabretta S, Barbagallo F, Capurso G, Pilozzi E, Geremia R, Delle Fave G, Sette C. Gemcitabine triggers a pro-survival response in pancreatic cancer cells through activation of the MNK2/eIF4E pathway. Oncogene. 2013;32:2848–2857. - PubMed
-
- Brown MC, Bryant JD, Dobrikova EY, Shveygert M, Bradrick SS, Chandramohan V, Bigner DD, Gromeier M. Induction of viral, 7-methyl-guanosine cap-independent translation and oncolysis by mitogen-activated protein kinase-interacting kinase-mediated effects on the serine/arginine-rich protein kinase. J Virol. 2014a;88:13135–13148. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brown MC, Dobrikov MI, Gromeier M. Mitogen-activated protein kinase-interacting kinase regulates mTOR/AKT signaling and controls the serine/arginine-rich protein kinase-responsive type 1 internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation and viral oncolysis. J Virol. 2014b;88:13149–13160. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chrestensen CA, Eschenroeder A, Ross WG, Ueda T, Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Fukunaga R, Sturgill TW. Loss of MNK function sensitizes fibroblasts to serum-withdrawal induced apoptosis. Genes to cells : devoted to molecular & cellular mechanisms. 2007;12:1133–1140. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

