Lipidomic Adaptations in White and Brown Adipose Tissue in Response to Exercise Demonstrate Molecular Species-Specific Remodeling
- PMID: 28178530
- PMCID: PMC5558157
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.01.038
Lipidomic Adaptations in White and Brown Adipose Tissue in Response to Exercise Demonstrate Molecular Species-Specific Remodeling
Abstract
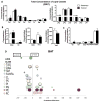
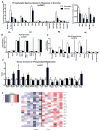
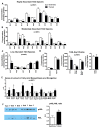
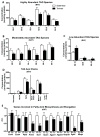
Exercise improves whole-body metabolic health through adaptations to various tissues, including adipose tissue, but the effects of exercise training on the lipidome of white adipose tissue (WAT) and brown adipose tissue (BAT) are unknown. Here, we utilize MS/MSALL shotgun lipidomics to determine the molecular signatures of exercise-induced adaptations to subcutaneous WAT (scWAT) and BAT. Three weeks of exercise training decrease specific molecular species of phosphatidic acid (PA), phosphatidylcholines (PC), phosphatidylethanolamines (PE), and phosphatidylserines (PS) in scWAT and increase specific molecular species of PC and PE in BAT. Exercise also decreases most triacylglycerols (TAGs) in scWAT and BAT. In summary, exercise-induced changes to the scWAT and BAT lipidome are highly specific to certain molecular lipid species, indicating that changes in tissue lipid content reflect selective remodeling in scWAT and BAT of both phospholipids and glycerol lipids in response to exercise training, thus providing a comprehensive resource for future studies of lipid metabolism pathways.
Keywords: adipose tissue; exercise; lipidomics.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Andersson A, Sjodin A, Olsson R, Vessby B. Effects of physical exercise on phospholipid fatty acid composition in skeletal muscle. The American journal of physiology. 1998;274:E432–438. - PubMed
-
- Body DR. The lipid composition of adipose tissue. Progress in lipid research. 1988;27:39–60. - PubMed
-
- Bonadonna RC, Saccomani MP, Seely L, Zych KS, Ferrannini E, Cobelli C, DeFronzo RA. Glucose transport in human skeletal muscle. The in vivo response to insulin. Diabetes. 1993;42:191–198. - PubMed
-
- Boss O, Samec S, Desplanches D, Mayet MH, Seydoux J, Muzzin P, Giacobino JP. Effect of endurance training on mRNA expression of uncoupling proteins 1, 2, and 3 in the rat. FASEB journal: official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology. 1998;12:335–339. - PubMed
-
- Burstein R, Zissholtz A, Zick-Bachar Y, Epstein Y, Shapiro Y, Karnieli E. Glucose uptake by adipocytes of obese rats: effect of one bout of acute exercise. Canadian journal of physiology and pharmacology. 1992;70:1473–1476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

