ERCC6L, a DNA helicase, is involved in cell proliferation and associated with survival and progress in breast and kidney cancers
- PMID: 28178669
- PMCID: PMC5522053
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14998
ERCC6L, a DNA helicase, is involved in cell proliferation and associated with survival and progress in breast and kidney cancers
Abstract
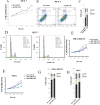
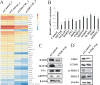
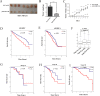
By analyzing 4987 cancer transcriptomes from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), we identified that excision repair cross-complementation group 6 like (ERCC6L), a newly discovered DNA helicase, is highly expressed in 12 solid cancers. However, its role and mechanism in tumorigenesis are largely unknown. In this study, we found that ERCC6L silencing by small interring RNA (siRNA) or short hairpin RNA (shRNA) significantly inhibited the proliferation of breast (MCF-7, MDA-MB-231) and kidney cancer cells (786-0). Furthermore, ERCC6L silencing induced cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase without affecting apoptosis. We then performed RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis after ERCC6L silencing and identified that RAB31 was markedly downregulated at both the transcriptional and translational levels. Its downstream protein, phosphorylated MAPK and CDK2 were also inhibited by ERCC6L silencing. The xenograft experiment showed that silencing of ERCC6L strikingly inhibited tumor growth from the 7th day after xenograft in nude mice. In addition, higher ERCC6L expression was found to be significantly associated with worse clinical survival in breast and kidney cancers. In conclusion, our results suggest that ERCC6L may stimulates cancer cell proliferation by promoting cell cycle through a way of RAB31-MAPK-CDK2, and it could be a potential biomarker for cancer prognosis and target for cancer treatment.
Keywords: MAPK; cancer; excision repair cross-complementation group 6 like; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicting financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
shRNA knockdown of DNA helicase ERCC6L expression inhibits human breast cancer growth.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Sep;18(3):3490-3496. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9317. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 30066865
-
ERCC6L that is up-regulated in high grade of renal cell carcinoma enhances cell viability in vitro and promotes tumor growth in vivo potentially through modulating MAPK signalling pathway.Cancer Gene Ther. 2019 Sep;26(9-10):323-333. doi: 10.1038/s41417-018-0064-8. Epub 2018 Nov 21. Cancer Gene Ther. 2019. PMID: 30459398
-
Knockdown of Rab7a suppresses the proliferation, migration, and xenograft tumor growth of breast cancer cells.Biosci Rep. 2019 Feb 5;39(2):BSR20180480. doi: 10.1042/BSR20180480. Print 2019 Feb 28. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 29769411 Free PMC article.
-
RAB10 overexpression promotes tumor growth and indicates poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 18;8(16):26434-26447. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15507. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28460436 Free PMC article.
-
ERCC6L promotes cell growth and invasion in human colorectal cancer.Oncol Lett. 2019 Jul;18(1):237-246. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10297. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31289493 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
PLK-1 Interacting Checkpoint Helicase, PICH, Mediates Cellular Oxidative Stress Response.Epigenomes. 2022 Oct 18;6(4):36. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes6040036. Epigenomes. 2022. PMID: 36278682 Free PMC article.
-
ERCC6L facilitates the progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by the binding of FOXM1 and KIF4A.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Feb 2;9(1):41. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01314-3. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 36726012 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of PICH promotes chromosome instability and cell death in triple-negative breast cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Jun 3;10(6):428. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1662-6. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31160555 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of hub genes for lymph node metastasis in patients with prostate cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Apr;24(8):4402-4414. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15098. Epub 2020 Mar 4. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32130760 Free PMC article.
-
Variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs) as modifiers of breast cancer risk in carriers of BRCA1 185delAG.Eur J Hum Genet. 2023 Feb;31(2):216-222. doi: 10.1038/s41431-022-01238-z. Epub 2022 Nov 25. Eur J Hum Genet. 2023. PMID: 36434258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu YJ, Chen XG, Li Y. Ercc6l, a gene of SNF2 family, may play a role in the teratogenic action of alcohol. Toxicol Lett. 2005;157:233–239. - PubMed
-
- Baumann C, Korner R, Hofmann K, Nigg EA. PICH, a centromere-associated SNF2 family ATPase, is regulated by Plk1 and required for the spindle checkpoint. Cell. 2007;128:101–114. - PubMed
-
- Helmke C, Becker S, Strebhardt K. The role of Plk3 in oncogenesis. Oncogene. 2016;35:135–147. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

