Programmable Genome Editing Tools and their Regulation for Efficient Genome Engineering
- PMID: 28179977
- PMCID: PMC5279741
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2016.12.006
Programmable Genome Editing Tools and their Regulation for Efficient Genome Engineering
Abstract
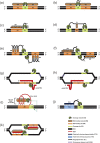
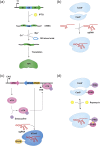
Targeted genome editing has become a powerful genetic tool for studying gene function or for modifying genomes by correcting defective genes or introducing genes. A variety of reagents have been developed in recent years that can generate targeted double-stranded DNA cuts which can be repaired by the error-prone, non-homologous end joining repair system or via the homologous recombination-based double-strand break repair pathway provided a suitable template is available. These genome editing reagents require components for recognizing a specific DNA target site and for DNA-cleavage that generates the double-stranded break. In order to reduce potential toxic effects of genome editing reagents, it might be desirable to control the in vitro or in vivo activity of these reagents by incorporating regulatory switches that can reduce off-target activities and/or allow for these reagents to be turned on or off. This review will outline the various genome editing tools that are currently available and describe the strategies that have so far been employed for regulating these editing reagents. In addition, this review will examine potential regulatory switches/strategies that can be employed in the future in order to provide temporal control for these reagents.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; Hammerhead ribozyme; Meganuclease; Regulatory switch; TALEN; Zinc finger nuclease.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
