Anterior Skull Base Glomangioma-Induced Osteomalacia
- PMID: 28180054
- PMCID: PMC5283168
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0036-1597599
Anterior Skull Base Glomangioma-Induced Osteomalacia
Abstract
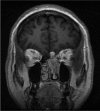
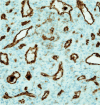
Oncogenic osteomalacia (OO) is an uncommon but treatable cause of osteomalacia related to tumor production of FGF23, usually caused by benign mesenchymal neoplasms. Paranasal sinus glomangiomas are a rare cause of OO, with only one previously reported case. Here we describe a second case (first reported in English) of paranasal sinus glomangioma-induced osteomalacia in a 42-year-old man. He presented with weakness and multiple spontaneous fractures, and was found to have an ethmoid sinus glomangioma with intracranial extension. The tumor was removed via endoscopic endonasal approach to the anterior skull base, which resulted in complete resolution of symptoms and no further evidence of disease 1 year postoperatively.
Keywords: glomangioma; glomus tumor; oncogenic osteomalacia; paranasal sinus tumor.
Figures


References
-
- Constantinidis J, Kiefer A, Reitnauer K, Iro H. Glomangioma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. Rhinology. 2000;38(03):136–139. - PubMed
-
- Tsuneyoshi M, Enjoji M. Glomus tumor: a clinicopathologic and electron microscopic study. Cancer. 1982;50(08):1601–1607. - PubMed
-
- Fu Y S, Perzin K H. Non-epithelial tumors of the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, and nasopharynx: a clinicopathologic study. I. General features and vascular tumors. Cancer. 1974;33(05):1275–1288. - PubMed
-
- Wang T, Qu S, Ye L. [Sinonasal glomus tumour-induced osteomalacia: a case report] [in Chinese] Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014;49(08):691–692. - PubMed
-
- Beech T J, Rokade A, Gittoes N, Johnson A P. A haemangiopericytoma of the ethmoid sinus causing oncogenic osteomalacia: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;36(10):956–958. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

