Genome-wide association study for performance traits in chickens using genotype by sequencing approach
- PMID: 28181508
- PMCID: PMC5299454
- DOI: 10.1038/srep41748
Genome-wide association study for performance traits in chickens using genotype by sequencing approach
Abstract
Performance traits are economically important and are targets for selection in breeding programs, especially in the poultry industry. To identify regions on the chicken genome associated with performance traits, different genomic approaches have been applied in the last years. The aim of this study was the application of CornellGBS approach (134,528 SNPs generated from a PstI restriction enzyme) on Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) in an outbred F2 chicken population. We have validated 91.7% of these 134,528 SNPs after imputation of missed genotypes. Out of those, 20 SNPs were associated with feed conversion, one was associated with body weight at 35 days of age (P < 7.86E-07) and 93 were suggestively associated with a variety of performance traits (P < 1.57E-05). The majority of these SNPs (86.2%) overlapped with previously mapped QTL for the same performance traits and some of the SNPs also showed novel potential QTL regions. The results obtained in this study suggests future searches for candidate genes and QTL refinements as well as potential use of the SNPs described here in breeding programs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
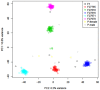
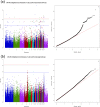

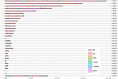
Similar articles
-
Unraveling genomic associations with feed efficiency and body weight traits in chickens through an integrative approach.BMC Genet. 2019 Nov 6;20(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12863-019-0783-3. BMC Genet. 2019. PMID: 31694549 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of quantitative trait loci for body temperature, body weight, breast yield, and digestibility in an advanced intercross line of chickens under heat stress.Genet Sel Evol. 2015 Dec 17;47:96. doi: 10.1186/s12711-015-0176-7. Genet Sel Evol. 2015. PMID: 26681307 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of QTL for traits related to adaptation to sub-optimal climatic conditions in chickens.Genet Sel Evol. 2017 Apr 20;49(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12711-017-0314-5. Genet Sel Evol. 2017. PMID: 28427323 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study of body weight in Wenshang Barred chicken based on the SLAF-seq technology.J Appl Genet. 2018 Aug;59(3):305-312. doi: 10.1007/s13353-018-0452-7. Epub 2018 Jun 27. J Appl Genet. 2018. PMID: 29946990 Review.
-
The study of candidate genes in the improvement of egg production in ducks - a review.Poult Sci. 2022 Jul;101(7):101850. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.101850. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Poult Sci. 2022. PMID: 35544958 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GBS-MeDIP: A protocol for parallel identification of genetic and epigenetic variation in the same reduced fraction of genomes across individuals.STAR Protoc. 2022 Mar 3;3(1):101202. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2022.101202. eCollection 2022 Mar 18. STAR Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35257114 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association studies targeting the yield of extraembryonic fluid and production traits in Russian White chickens.BMC Genomics. 2019 Apr 4;20(1):270. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5605-5. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30947682 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association and selective sweep analyses reveal genetic loci for FCR of egg production traits in ducks.Genet Sel Evol. 2021 Dec 20;53(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12711-021-00684-5. Genet Sel Evol. 2021. PMID: 34930109 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association Study of Egg Production Traits in Shuanglian Chickens Using Whole Genome Sequencing.Genes (Basel). 2023 Nov 25;14(12):2129. doi: 10.3390/genes14122129. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136951 Free PMC article.
-
Association analysis of production traits of Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica) using restriction-site associated DNA sequencing.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 2;13(1):21307. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-48293-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38042890 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fulton J. E. Genomic selection for poultry breeding. Anim. Front. 2, 30–36 (2012).
-
- Blackburn H. D. The National Animal Germplasm Program: challenges and opportunities for poultry genetic resources. Poult. Sci. 85, 210–215 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Ambo M. et al.. Genetic linkage maps of chicken chromosomes 6, 7, 8, 11 and 13 from a Brazilian resource population. Sci. Agric. 65, 447–452 (2008).
-
- Ambo M. et al.. Quantitative trait loci for performance traits in a broiler x layer cross. Anim. Genet. 40, 200–8 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Nones K. et al.. Mapping QTLs on chicken chromosome 1 for performance and carcass traits in a broiler x layer cross. Anim. Genet. 37, 95–100 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

