Basic concepts and recent advances in nanogels as carriers for medical applications
- PMID: 28181831
- PMCID: PMC8240973
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2016.1276232
Basic concepts and recent advances in nanogels as carriers for medical applications
Abstract
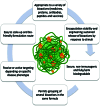
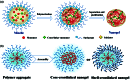
Nanogels in biomedical field are promising and innovative materials as dispersions of hydrogel nanoparticles based on crosslinked polymeric networks that have been called as next generation drug delivery systems due to their relatively high drug encapsulation capacity, uniformity, tunable size, ease of preparation, minimal toxicity, stability in the presence of serum, and stimuli responsiveness. Nanogels show a great potential in chemotherapy, diagnosis, organ targeting and delivery of bioactive substances. The main subjects reviewed in this article concentrates on: (i) Nanogel assimilation in the nanomedicine domain; (ii) Features and advantages of nanogels, the main characteristics, such as: swelling capacity, stimuli sensitivity, the great surface area, functionalization, bioconjugation and encapsulation of bioactive substances, which are taken into account in designing the structures according to the application; some data on the advantages and limitations of the preparation techniques; (iii) Recent progress in nanogels as a carrier of genetic material, protein and vaccine. The majority of the scientific literature presents the multivalency potential of bioconjugated nanogels in various conditions. Today's research focuses over the overcoming of the restrictions imposed by cost, some medical requirements and technological issues, for nanogels' commercial scale production and their integration as a new platform in biomedicine.
Keywords: Nanogel; drug release; genetic material; nanocarrier; physical and chemical cross linking; protein and vaccine delivery; response to external stimuli.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflicts of interest.
Romanian National Authority for Scientific Research, CNCS-UEFISCDI, project number PNII-RU-TE-2014-4-0294 “Novel hydrogels synthesis with defined 3D functionality and biodegradable characteristics for bioapplications”
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nanogel-based Transdermal Drug Delivery System: A Therapeutic Strategy with Under Discussed Potential.Curr Top Med Chem. 2023;23(1):44-61. doi: 10.2174/1568026622666220818112728. Curr Top Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 35984019 Review.
-
Biomedicine Innovations and Its Nanohydrogel Classifications.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 18;14(12):2839. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122839. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New progress and prospects: The application of nanogel in drug delivery.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016 Mar;60:560-568. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.11.041. Epub 2015 Nov 18. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016. PMID: 26706564 Review.
-
Chemical, physical, and biological stimuli-responsive nanogels for biomedical applications (mechanisms, concepts, and advancements): A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jan 31;226:535-553. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.076. Epub 2022 Dec 12. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 36521697 Review.
-
A review of polymeric colloidal nanogels in transdermal drug delivery.Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(20):2801-13. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666150428142920. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 25925117 Review.
Cited by
-
Cosmetic, Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications of Fish Gelatin/Hydrolysates.Mar Drugs. 2021 Mar 8;19(3):145. doi: 10.3390/md19030145. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33800149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of the Core Formulation on Features and Drug Delivery Ability of Carbamate-Based Nanogels.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 10;21(18):6621. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186621. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32927733 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Nanogels: Current Trends and Future Outlook.Gels. 2021 Mar 29;7(2):36. doi: 10.3390/gels7020036. Gels. 2021. PMID: 33805279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physically stimulus-responsive nanoparticles for therapy and diagnosis.Front Chem. 2022 Sep 14;10:952675. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.952675. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 36186605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier: Advances in Nanoparticle Technology for Drug Delivery in Neuro-Oncology.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 9;23(8):4153. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084153. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35456971 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akiyama E, Morimoto N, Kujawa P. (2007). Self-assembled nanogels of cholesteryl-modified polysaccharides: effect of the polysaccharide structure on their association characteristics in the dilute and semidilute regimes. Biomacromolecules 8:2366–73 - PubMed
-
- Akiyoshi K, Deguchi N, Moriguchi N. (1993). Self-aggregates of hydrophobized polysaccharides in water. Formation and characteristics of nanoparticles. Macromolecules 26:3062–8
-
- Akiyoshi K, Kang EC, Kuromada S. (2000). Controlled association of amphiphilic polymers in water: thermosensitive nanoparticles formed by self-assembly of hydrophobically modified pullulans and poly(N-isopropylacrylamides). Macromolecules 33:3244–9
-
- Akiyoshi K, Kobayashi S, Shichibe S, et al. . (1998). Self-assembled hydrogel nanoparticle of cholesterol-bearing pullulan as a carrier of protein drugs: complexation and stabilization of insulin. J Control Release 54:313–20 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
