A possible role of the Infant/Toddler Sensory Profile in screening for autism: a proof-of-concept study in the specific sample of prematurely born children with birth weights <1,500 g
- PMID: 28182143
- PMCID: PMC5279831
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S123066
A possible role of the Infant/Toddler Sensory Profile in screening for autism: a proof-of-concept study in the specific sample of prematurely born children with birth weights <1,500 g
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to explore the potential of the Infant/Toddler Sensory Profile (ITSP) as a screening tool for autism spectrum disorders (ASD) in prematurely born children.
Methods: Parents of 157 children with birth weights <1,500 g (aged 2 years, corrected for prematurity; 88 boys, 69 girls) completed a screening battery that included the ITSP, Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT), and the Communication and Symbolic Behavior Scales Developmental Profile Infant-Toddler Checklist (CSBS-DP-ITC). Children with known disabilities were excluded. All the children who were screened positive on any of the screening tools subsequently underwent clinical examination including the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule.
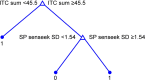
Results: We used classification trees to answer the question whether ITSP (or some of its subscales) could be combined with the M-CHAT and/or the CSBS-DP-ITC or its subscales into an effective ASD screening tool. Using the CSBS-DP-ITC, overall score, and the Sensation Seeking subscale of the ITSP, we obtained a screening tool that was able to identify all of the ASD children in our sample (confirmed by cross-validation). The proposed screening tool is scored as follows: 1) if the overall CSBS-DP-ITC value is <45.5, then the screening is positive; 2) if the overall CSBS-DP-ITC value is ≥45.5 and the z-score of the Sensation Seeking subscale of ITSP is ≥1.54, then the screening is positive; 3) otherwise, the screening is negative.
Conclusion: The use of CSBS-DP-ITC in combination with the Sensation Seeking subscale of the ITSP improved the accuracy of autism screening in preterm children.
Keywords: Communication and Symbolic Behavior Scales Developmental Profile Infant-Toddler Checklist; Infant/Toddler Sensory Profile; Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers; autism spectrum disorders; preterm children; screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of Early Warning Signs in Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Review.Children (Basel). 2021 Feb 22;8(2):164. doi: 10.3390/children8020164. Children (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33671540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of three screening tests for autism in preterm children with birth weights less than 1,500 grams.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014 Nov 17;10:2201-8. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S72921. eCollection 2014. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014. PMID: 25484588 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for autism in preterm children with extremely low and very low birth weight.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014 Feb 11;10:277-82. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S57057. eCollection 2014. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014. PMID: 24627633 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing early communication behaviours: structure and validity of the Communication and Symbolic Behaviour Scales-Developmental Profile (CSBS-DP) in 12-month-old infants.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2010 Sep-Oct;45(5):572-85. doi: 10.3109/13682820903277944. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2010. PMID: 19886849
-
Screening for autism in young children: The Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT) and other measures.Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2005;11(3):253-62. doi: 10.1002/mrdd.20072. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2005. PMID: 16161090 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnosing Autism Spectrum Disorder in Toddlers Born Very Preterm: Estimated Prevalence and Usefulness of Screeners and the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS).J Autism Dev Disord. 2021 May;51(5):1508-1527. doi: 10.1007/s10803-020-04573-6. J Autism Dev Disord. 2021. PMID: 32757085
-
Explaining individual differences in infant visual sensory seeking.Infancy. 2020 Sep;25(5):677-698. doi: 10.1111/infa.12356. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Infancy. 2020. PMID: 32748567 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal brain growth and infant autistic traits.Mol Autism. 2024 Feb 28;15(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13229-024-00586-5. Mol Autism. 2024. PMID: 38419120 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Early Physiotherapy in an Infant With a High Risk of Developmental Delay.Cureus. 2021 Jul 23;13(7):e16581. doi: 10.7759/cureus.16581. eCollection 2021 Jul. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34434678 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Early Warning Signs in Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Review.Children (Basel). 2021 Feb 22;8(2):164. doi: 10.3390/children8020164. Children (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33671540 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dunn W. Infant/Toddler Sensory Profile: User’s Manual. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corporation; 2002.
-
- Dunn W, Westman K. The sensory profile: the performance of a national sample of children without disabilities. Am J Occup Ther. 1997;51(1):25–34. - PubMed
-
- Kanner L. Autistic disturbances of affective contact. Nervous Child. 1943;2:217–250. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Sasson A, Hen L, Fluss R, Cermak SA, Engel-Yeger B, Gal E. A meta-analysis of sensory modulation symptoms in individuals with autism spectrum disorders. J Autism Dev Disord. 2009;39:1–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

