Enhanced and long term immunogenicity of a Her-2/neu multi-epitope vaccine conjugated to the carrier CRM197 in conjunction with the adjuvant Montanide
- PMID: 28183282
- PMCID: PMC5301331
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-017-3098-7
Enhanced and long term immunogenicity of a Her-2/neu multi-epitope vaccine conjugated to the carrier CRM197 in conjunction with the adjuvant Montanide
Abstract
Background: We previously identified three short single peptides (P4, P6 and P7) representing different B-cell epitopes on the extracellular domain of Her-2/neu for a vaccine that was tested in a phase-I clinical trial. Here we describe the improvement of the multi peptide vaccine by fusing the single peptides to a hybrid peptide P467.
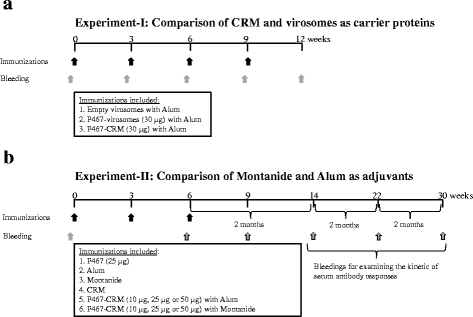
Methods: After coupling to either virosomes or to diphtheria toxoid CRM197 (CRM), the hybrid peptide was tested in different concentrations in combination with either Montanide or Aluminium hydroxide (Alum) in preclinical studies.
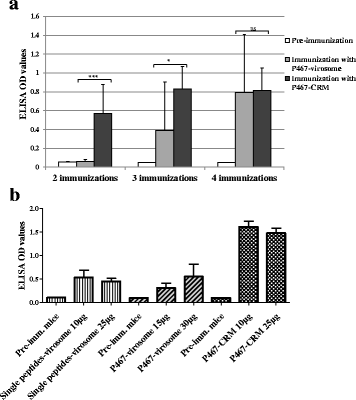
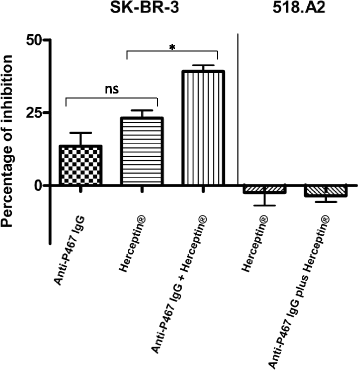
Results: Already low amount (10 μg) of P467 conjugated to CRM led to faster onset of high antibody levels compared to the P467-virosome. The formulation P467-CRM-Montanide induced higher serum IgG antibody titers, compared with P467-CRM-Alum, as examined by ELISA using recombinant Her-2/neu or Her-2/neu natively expressed on the tumor cell line SK-BR-3. Compared to P467-CRM-Alum, higher in vitro production of IL-2 and IFNγ in the Montanide-immunized mice was induced after re-stimulation of splenocytes with CRM but also with P467, indicating a clear Th1-biased response. In contrast to the single B cell peptides, the hybrid peptide led to T cell proliferation and cytokine production as CD4 T cell epitopes were generated in the fusion region of the single peptides P4 and P6 or P6 and P7. Additionally, a significantly higher proportion IFNγ-producing CD8+ T cells was found in the P467-CRM-Montanide immunized mice, probably by Montanide-driven bystander activation. Importantly, anti-P467 IgG antibodies exhibited anti-tumor properties and the combination of anti-P467 specific IgG with Herceptin® was found to inhibit the proliferation of Her-2/neu-overexpressing cell line SK-BR-3 in a significantly higher capacity than Herceptin® alone.
Conclusions: Fusion of the B cell peptides has led to additional generation of CD4 T cell epitopes, and this P467-multi epitope vaccine was found to induce polyclonal antibody responses with anti-proliferative capacity against Her-2/neu. The hybrid vaccine together with Montanide induced higher and long-lasting antibody levels, Th1-biased cellular responses being superior to vaccination with the single B cell peptides. This vaccine formulation is now planned to be evaluated in a phase Ib/II study in Her-2/neu overexpressing cancer patients.
Keywords: Adjuvant; Her-2/neu; Humoral and cellular response; Hybrid peptide; Mice; Th1-deriving response.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Delayed tumor onset and reduced tumor growth progression after immunization with a Her-2/neu multi-peptide vaccine and IL-12 in c-neu transgenic mice.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007 Nov;106(1):29-38. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9469-4. Epub 2007 Jan 3. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007. PMID: 17203384
-
A virosomal formulated Her-2/neu multi-peptide vaccine induces Her-2/neu-specific immune responses in patients with metastatic breast cancer: a phase I study.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010 Feb;119(3):673-83. doi: 10.1007/s10549-009-0666-9. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010. PMID: 20092022 Clinical Trial.
-
Inhibition of tumor cell growth by antibodies induced after vaccination with peptides derived from the extracellular domain of Her-2/neu.Int J Cancer. 2003 Dec 20;107(6):976-83. doi: 10.1002/ijc.11485. Int J Cancer. 2003. PMID: 14601058
-
Peptide emulsions in incomplete Freund's adjuvant create effective nurseries promoting egress of systemic CD4+ and CD8+ T cells for immunotherapy of cancer.J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Sep;10(9):e004709. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-004709. J Immunother Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36939214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaccination for the prevention and treatment of breast cancer with special focus on Her-2/neu peptide vaccines.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013 Feb;138(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s10549-013-2410-8. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013. PMID: 23340862 Review.
Cited by
-
Current progress in the development of prophylactic and therapeutic vaccines.Sci China Life Sci. 2023 Apr;66(4):679-710. doi: 10.1007/s11427-022-2230-4. Epub 2022 Dec 2. Sci China Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36469218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of the B cell cancer vaccine HER-vaxx for the treatment of her-2 expressing cancers.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 12;12:939356. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.939356. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36578947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Tumor-Associated Antigen HER2/neu in Tumor Development and the Different Approaches for Using It in Treatment: Many Choices and Future Directions.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 14;14(24):6173. doi: 10.3390/cancers14246173. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide-Based Vaccines: Current Progress and Future Challenges.Chem Rev. 2020 Mar 25;120(6):3210-3229. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00472. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Chem Rev. 2020. PMID: 31804810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of a Human T Cell-Targeted Multi-Epitope Vaccine for Q Fever in Animal Models of Coxiella burnetii Immunity.Front Immunol. 2022 May 16;13:901372. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.901372. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35651616 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

