Rapid and sensitive real-time assay for the detection of respiratory syncytial virus using RT-SIBA®
- PMID: 28183291
- PMCID: PMC5301360
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-017-2227-x
Rapid and sensitive real-time assay for the detection of respiratory syncytial virus using RT-SIBA®
Abstract
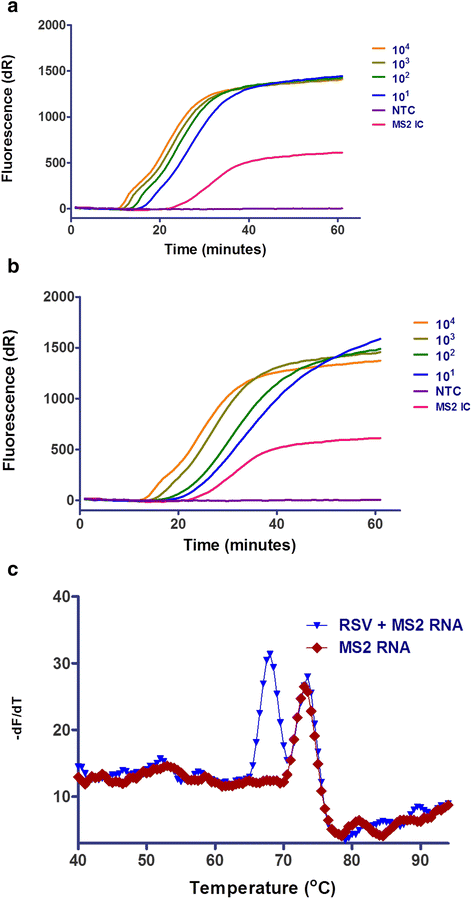
Background: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is one of the most common causes of respiratory tract infections among young children and the elderly. Timely and accurate diagnosis of respiratory tract infections improves patient care and minimizes unnecessary prescriptions of antibiotics. We sought to develop a rapid nucleic acid tests for the detection of RSV within minutes, while retaining the high sensitivity achieved with RT-PCR.
Methods: We developed and evaluated a reverse transcription isothermal nucleic acid amplification method, reverse transcription strand invasion based amplification (RT-SIBA), for the rapid detection of RSV.
Results: The developed RT-SIBA assay showed good sensitivity by detecting as few as 10 copies of RSV RNA within 20 min compared with reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, which took approximately 2 h. The performance of the RT-SIBA RSV assay was further investigated using nasopharyngeal swab specimens. The RT-SIBA assay had a sensitivity of 100% (25/25) and a specificity of 100% (15/15).
Conclusion: RT-SIBA did not require highly purified RNA for the rapid detection of RSV and was therefore compatible with rapid specimen processing methods. This reduces the complexity of specimen preparation and further shortens the total amount of time needed to detect RSV in clinical specimens. The developed RT-SIBA assay for RSV could be a useful tool for prompt management of this infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the reverse transcription strand invasion based amplification (RT-SIBA) RSV assay, a rapid molecular assay for the detection of respiratory syncytial virus.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019 Sep;95(1):55-58. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2019.04.006. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31160164
-
[Detecting human respiratory syncytial virus in respiratory samples collected from children with acute respiratory infections by reverse transcription-loop mediated isothermal amplification].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Apr;51(4):270-5. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23927800 Chinese.
-
Development of a reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification assay for rapid detection of human respiratory syncytial virus.Mol Cell Probes. 2019 Jun;45:8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2019.03.005. Epub 2019 Mar 25. Mol Cell Probes. 2019. PMID: 30922817
-
Underascertainment of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection in Adults Due to Diagnostic Testing Limitations: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-analysis.J Infect Dis. 2023 Jul 14;228(2):173-184. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad012. J Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36661222 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric Respiratory Syncytial Virus Diagnostic Testing Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Infect Dis. 2023 Nov 28;228(11):1516-1527. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad185. J Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37285396 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Electrochemical Immunosensors Based on Screen-Printed Gold and Glassy Carbon Electrodes: Comparison of Performance for Respiratory Syncytial Virus Detection.Biosensors (Basel). 2020 Nov 13;10(11):175. doi: 10.3390/bios10110175. Biosensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33202922 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory syncytial virus: A review of current basic and clinical knowledge.Qatar Med J. 2024 Dec 24;2024(4):56. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2024.56. eCollection 2024. Qatar Med J. 2024. PMID: 39931346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Detection of Streptococcus pyogenes by Strand Invasion Based Amplification Assay.Mol Diagn Ther. 2018 Oct;22(5):595-602. doi: 10.1007/s40291-018-0346-8. Mol Diagn Ther. 2018. PMID: 29967988 Free PMC article.
-
Manually pressurized droplet digital PCR chip for rapid SARS-CoV-2 diagnostics.Biomicrofluidics. 2024 Feb 27;18(1):014106. doi: 10.1063/5.0180394. eCollection 2024 Jan. Biomicrofluidics. 2024. PMID: 38420041 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Different Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction-Based Methods for Wastewater Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2: Exploratory Study.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024 Aug 19;10:e53175. doi: 10.2196/53175. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024. PMID: 39158943 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Piedimonte G. RSV infections: state of the art. Cleve Clin J Med. 2015;82(11 Suppl 1):S13–8. - PubMed
-
- de-Paris F, Beck C, de Souza Nunes L, Pinheiro AM, Paiva RM, da Silva Menezes D, Pires MR, dos Santos RP, de Souza Kuchenbecker R, Barth AL. Evaluation of respiratory syncytial virus group A and B genotypes among nosocomial and community-acquired pediatric infections in southern Brazil. Virol J. 2014;11(1):1–6. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-11-36. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

