Carbamylation of vimentin is inducible by smoking and represents an independent autoantigen in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 28183721
- PMCID: PMC5530349
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210059
Carbamylation of vimentin is inducible by smoking and represents an independent autoantigen in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objectives: Smoking has been connected to citrullination of antigens and formation of anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies (ACPAs) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Since smoking can modify proteins by carbamylation (formation of homocitrulline), this study was conducted to investigate these effects on vimentin in animal models and RA.
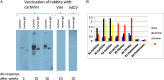
Methods: The efficiency of enzymatic carbamylation of vimentin was characterised. B-cell response was investigated after immunisation of rabbits with different vimentin isoforms. Effects of tobacco smoke exposure on carbamylation of vimentin and formation of autoantibodies were analysed in mice. The antibody responses against isoforms of vimentin were characterised with respect to disease duration and smoking status of patients with RA.
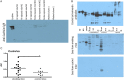
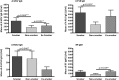
Results: Enzymatic carbamylation of vimentin was efficiently achieved. Subsequent citrullination of vimentin was not disturbed by homocitrullination. Sera from rabbits immunised with carbamylated vimentin (carbVim), in addition to carbVim also recognised human IgG-Fc showing rheumatoid factor-like reactivity. Smoke-exposed mice contained detectable amounts of carbVim and developed a broad immune response against carbamylated antigens. Although the prevalence of anti-carbamylated antibodies in smokers and non-smokers was similar, the titres of carbamylated antibodies were significantly increased in sera of smoking compared with non-smoking RA. CarbVim antibodies were observed independently of ACPAs in early phases of disease and double-positive patients for anti-mutated citrullinated vimentin (MCV) and anti-carbVim antibodies showed an extended epitope recognition pattern towards MCV.
Conclusions: Carbamylation of vimentin is inducible by cigarette smoke exposure. The polyclonal immune response against modified antigens in patients with RA is not exclusively citrulline-specific and carbamylation of antigens could be involved in the pathogenesis of disease.
Trial registration number: ISRCTN36745608; EudraCT Number: 2006-003146-41.
Keywords: DAS28; Rheumatoid Arthritis; Smoking.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: HB is an employee of Orgentec Diagnostika GmbH, Mainz, Germany; test kits were kindly provided by Orgentec.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Carbamylated vimentin represents a relevant autoantigen in Latin American (Cuban) rheumatoid arthritis patients.Rheumatol Int. 2016 Jun;36(6):781-91. doi: 10.1007/s00296-016-3472-9. Epub 2016 Apr 2. Rheumatol Int. 2016. PMID: 27038800 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation and citrullination modifies vimentin to a novel autoantigen for rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Aug;56(8):2503-11. doi: 10.1002/art.22817. Arthritis Rheum. 2007. PMID: 17665451
-
Breach of autoreactive B cell tolerance by post-translationally modified proteins.Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Aug;76(8):1449-1457. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210772. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017. PMID: 28442530
-
Pitfalls in the detection of citrullination and carbamylation.Autoimmun Rev. 2018 Feb;17(2):136-141. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.11.017. Epub 2017 Dec 2. Autoimmun Rev. 2018. PMID: 29203292 Review.
-
Redox-Mediated Carbamylation As a Hapten Model Applied to the Origin of Antibodies to Modified Proteins in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022 Mar;36(7-9):389-409. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0064. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022. PMID: 33906423 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of the association of baseline anti-CarbV and anti-MCV antibodies with response to treatment and radiographic progression in an RA population treated with either methotrexate or baricitinib: post-hoc analyses from RA-BEGIN.Arthritis Res Ther. 2020 Aug 18;22(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02284-y. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32811536 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of anti-carbamylated protein antibodies on disease activity and joint erosions in seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2023 Dec;43(12):2245-2250. doi: 10.1007/s00296-023-05445-9. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Rheumatol Int. 2023. PMID: 37697044
-
Autoimmunity, inflammation, and dysbiosis mutually govern the transition from the preclinical to the clinical stage of rheumatoid arthritis.Immunol Res. 2018 Dec;66(6):696-709. doi: 10.1007/s12026-018-9048-x. Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 30498956 Review.
-
Autoantibodies in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Prognosis of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 14;9:3168. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03168. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30693002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vasculitis in Africa.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2018 Feb 21;20(2):4. doi: 10.1007/s11926-018-0711-y. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29464351 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hensvold AH, Magnusson PK, Joshua V, et al. . Environmental and genetic factors in the development of anticitrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs) and ACPA-positive rheumatoid arthritis: an epidemiological investigation in twins. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:375–80. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203947 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

