Extracellular RNAs Are Associated With Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Phenotypes
- PMID: 28183786
- PMCID: PMC5360281
- DOI: 10.2337/dc16-1354
Extracellular RNAs Are Associated With Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Phenotypes
Abstract
Objective: Insulin resistance (IR) is a hallmark of obesity and metabolic disease. Circulating extracellular RNAs (ex-RNAs), stable RNA molecules in plasma, may play a role in IR, though most studies on ex-RNAs in IR are small. We sought to characterize the relationship between ex-RNAs and metabolic phenotypes in a large community-based human cohort.
Research design and methods: We measured circulating plasma ex-RNAs in 2,317 participants without diabetes in the Framingham Heart Study (FHS) Offspring Cohort at cycle 8 and defined associations between ex-RNAs and IR (measured by circulating insulin level). We measured association between candidate ex-RNAs and markers of adiposity. Sensitivity analyses included individuals with diabetes. In a separate cohort of 90 overweight/obese youth, we measured selected ex-RNAs and metabolites. Biology of candidate microRNAs was investigated in silico.
Results: The mean age of FHS participants was 65.8 years (56% female), with average BMI 27.7 kg/m2; participants in the youth cohort had a mean age of 15.5 years (60% female), with mean BMI 33.8 kg/m2. In age-, sex-, and BMI-adjusted models across 391 ex-RNAs in FHS, 18 ex-RNAs were associated with IR (of which 16 were microRNAs). miR-122 was associated with IR and regional adiposity in adults and IR in children (independent of metabolites). Pathway analysis revealed metabolic regulatory roles for miR-122, including regulation of IR pathways (AMPK, target of rapamycin signaling, and mitogen-activated protein kinase).
Conclusions: These results provide translational evidence in support of an important role of ex-RNAs as novel circulating factors implicated in IR.
© 2017 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
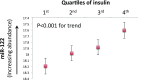
References
-
- Arner P, Kulyté A. MicroRNA regulatory networks in human adipose tissue and obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2015;11:276–288 - PubMed
-
- Ortega FJ, Mercader JM, Catalán V, et al. Targeting the circulating microRNA signature of obesity. Clin Chem 2013;59:781–792 - PubMed
-
- Ortega FJ, Mercader JM, Moreno-Navarrete JM, et al. Surgery-induced weight loss is associated with the downregulation of genes targeted by microRNAs in adipose tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015;100:E1467–E1476 - PubMed
-
- Ortega FJ, Mercader JM, Moreno-Navarrete JM, et al. Profiling of circulating microRNAs reveals common microRNAs linked to type 2 diabetes that change with insulin sensitization. Diabetes Care 2014;37:1375–1383 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

