A low dose of droperidol decreases the desflurane concentration needed during breast cancer surgery: a randomized double-blinded study
- PMID: 28184263
- PMCID: PMC5296383
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2017.70.1.27
A low dose of droperidol decreases the desflurane concentration needed during breast cancer surgery: a randomized double-blinded study
Abstract
Background: Droperidol (DHB) reportedly reduces the dose of propofol needed to achieve hypnosis when anesthesia is induced and decreases the bispectral index (BIS) in propofol-sedated patients during spinal anesthesia. We reported previously that supplemental DHB decreased the BIS after the administration of sevoflurane and remifentanil. This study investigated the effect of DHB on desflurane (DES) consumption in a clinical setting.
Methods: We conducted a prospective, randomized double-blinded study of 35 women with American Society of Anesthesiologist physical status I or II who underwent a mastectomy. Either DHB (20 µg/kg) or a saline placebo was administered to patients 30 min after the induction of anesthesia. A blinded anesthesiologist maintained a BIS value of 50 during anesthesia by modulating inhaled DES concentrations that changed 0.5% at 2.5 min intervals and maintained analgesia via the constant administration of remifentanil by referring to vital signs. The primary endpoint was the effect of DHB on DES consumption. The secondary endpoints included blood circulatory parameters, the time from the end of surgery to extubation, and discharge time between the groups.
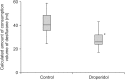
Results: The characteristics of the patients did not differ between the groups. The DHB group used a mean of 27.2 ± 6.0 ml of DES compared with 41.4 ± 9.5 ml by the placebo group (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: A small dose of DHB reduced the DES concentration needed to maintain a BIS of 50. Our results show that DHB reduced the consumption of DES without adverse effects.
Keywords: Bispectral index; Desflurane; Droperidol; General anesthesia.
Figures


References
-
- Nakao S, Hatano K, Sumi C, Masuzawa M, Sakamoto S, Ikeda S, et al. Sevoflurane causes greater QTc interval prolongation in elderly patients than in younger patients. Anesth Analg. 2010;110:775–779. - PubMed
-
- Halloran K, Barash PG. Inside the black box: current policies and concerns with the United States Food and Drug Administration's highest drug safety warning system. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2010;23:423–427. - PubMed
-
- Nuttall GA, Malone AM, Michels CA, Trudell LC, Renk TD, Marienau ME, et al. Does low-dose droperidol increase the risk of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia or death in the surgical patient? Anesthesiology. 2013;118:382–386. - PubMed
-
- Staikou C, Stamelos M, Stavroulakis E. Impact of anaesthetic drugs and adjuvants on ECG markers of torsadogenicity. Br J Anaesth. 2014;112:217–230. - PubMed
-
- Adachi YU, Uchihashi Y, Watanabe K, Satoh T. Small dose midazolam or droperidol reduces the hypnotic dose of propofol at the induction of anaesthesia. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2000;17:126–131. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

