Effects of preanesthetic dexmedetomidine on hemodynamic responses to endotracheal intubation in elderly patients undergoing treatment for hypertension: a randomized, double-blinded trial
- PMID: 28184265
- PMCID: PMC5296386
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2017.70.1.39
Effects of preanesthetic dexmedetomidine on hemodynamic responses to endotracheal intubation in elderly patients undergoing treatment for hypertension: a randomized, double-blinded trial
Abstract
Background: Dexmedetomidine is an alpha-2 adrenergic agonist with sedative, anxiolytic, and analgesic properties. This study was designed to evaluate the inhibitory effects of preoperative administration of 0.5 µg/kg dexmedetomidine on hemodynamic responses caused by endotracheal intubation in elderly patients undergoing treatment for hypertension.
Methods: Forty elderly (≥ 65 years old) patients who had been receiving hypertension treatment, had American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status II, and were scheduled to undergo elective noncardiac surgery were randomly selected and assigned to 2 groups. Group C received normal saline and group D received 0.5 µg/kg dexmedetomidine intravenously over 10 min just before endotracheal intubation. Systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), mean arterial pressure (MAP), and heart rate (HR) were recorded preoperatively in the ward, immediately after study drug administration, and at 1, 3, and 5 min after endotracheal intubation.
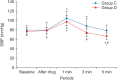
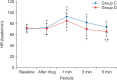
Results: Compared to group C, group D showed significantly lower SBP and MAP at 1, 3, and 5 min as well as significantly lower DBP and HR at 3 and 5 min after endotracheal intubation.
Conclusions: In elderly patients receiving hypertension treatment, a single preanesthetic dose of dexmedetomidine (0.5 µg/kg) effectively suppressed the hemodynamic responses to endotracheal intubation.
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine; Hemodynamics; Intubation; Preanesthetic medication.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The sedative effects and the attenuation of cardiovascular and arousal responses during anesthesia induction and intubation in pediatric patients: a randomized comparison between two different doses of preoperative intranasal dexmedetomidine.Paediatr Anaesth. 2014 Mar;24(3):275-81. doi: 10.1111/pan.12284. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Paediatr Anaesth. 2014. PMID: 24224515 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical evaluation of the effect of intravenous dexmedetomidine on the hemodynamic response to laryngoscopy and endotracheal intubation in patients undergoing thyroid surgeries.Anesth Essays Res. 2016 Sep-Dec;10(3):483-487. doi: 10.4103/0259-1162.179311. Anesth Essays Res. 2016. PMID: 27746537 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Esmolol and Dexmedetomidine for Suppression of Hemodynamic Response to Laryngoscopy and Endotracheal Intubation in Adult Patients Undergoing Elective General Surgery: A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Double-blinded Study.Anesth Essays Res. 2018 Jan-Mar;12(1):262-266. doi: 10.4103/aer.AER_226_17. Anesth Essays Res. 2018. PMID: 29628593 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine as an adjunct to anesthetic induction to attenuate hemodynamic response to endotracheal intubation in patients undergoing fast-track CABG.Ann Card Anaesth. 2010 Jan-Apr;13(1):16-21. doi: 10.4103/0971-9784.58829. Ann Card Anaesth. 2010. PMID: 20075530 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Dexmedetomidine on Maintaining Perioperative Hemodynamic Stability in Elderly Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Chin Med Sci J. 2023 Mar 31;38(1):1-10. doi: 10.24920/004088. Chin Med Sci J. 2023. PMID: 37066726
Cited by
-
Dexmedetomidine vs. Fentanyl-Midazolam Combination to Mitigate the Stress Response in Microlaryngoscopy: A Randomized Double-blind Clinical Trial.Anesth Pain Med. 2023 May 8;13(3):e135276. doi: 10.5812/aapm-135276. eCollection 2023 Jun. Anesth Pain Med. 2023. PMID: 38021325 Free PMC article.
-
Real-Time Monitoring of Blood Pressure Using Digitalized Pulse Arrival Time Calculation Technology for Prompt Detection of Sudden Hypertensive Episodes During Laryngeal Microsurgery: Retrospective Observational Study.J Med Internet Res. 2020 May 15;22(5):e13156. doi: 10.2196/13156. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 32412413 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical data presentation.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2017 Jun;70(3):267-276. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2017.70.3.267. Epub 2017 May 19. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2017. PMID: 28580077 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine for the prevention of postoperative delirium in elderly patients undergoing noncardiac surgery: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 16;14(8):e0218088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218088. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31419229 Free PMC article.
-
Factors to bear in mind regarding the use of dexmedetomidine.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2017 Jun;70(3):233-234. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2017.70.3.233. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2017. PMID: 28580071 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Virtanen R, Savola JM, Saano V, Nyman L. Characterization of the selectivity, specificity and potency of medetomidine as an alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988;150:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Yildiz M, Tavlan A, Tuncer S, Reisli R, Yosunkaya A, Otelcioglu S. Effect of dexmedetomidine on haemodynamic responses to laryngoscopy and intubation : perioperative haemodynamics and anaesthetic requirements. Drugs R D. 2006;7:43–52. - PubMed
-
- Prys-Roberts C, Greene LT, Meloche R, Foëx P. Studies of anaesthesia in relation to hypertension. II. Haemodynamic consequences of induction and endotracheal intubation. Br J Anaesth. 1971;43:531–547. - PubMed
-
- Shribman AJ, Smith G, Achola KJ. Cardiovascular and catecholamine responses to laryngoscopy with and without tracheal intubation. Br J Anaesth. 1987;59:295–299. - PubMed
-
- Edwards ND, Alford AM, Dobson PM, Peacock JE, Reilly CS. Myocardial ischaemia during tracheal intubation and extubation. Br J Anaesth. 1994;73:537–539. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

