The effect of ketorolac and dexamethasone on the incidence of sore throat in women after thyroidectomy: a prospective double-blinded randomized trial
- PMID: 28184269
- PMCID: PMC5296390
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2017.70.1.64
The effect of ketorolac and dexamethasone on the incidence of sore throat in women after thyroidectomy: a prospective double-blinded randomized trial
Abstract
Background: We evaluated the effect of two drugs with anti-inflammatory action, dexamethasone and ketorolac, on reduction of postoperative sore throat (POST) after general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation in patients undergoing thyroidectomy.
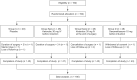
Methods: One hundred and ninety-two female patients scheduled to undergo general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation for thyroidectomy were enrolled in this prospective study. Participants were randomly allocated to receive intravenous medication; placebo (Group C, n = 45), ketorolac 30 mg immediately before intubation (Group Kpre, n = 47), ketorolac 30 mg at the end of surgery (Group Kpost, n = 45) and dexamethasone 10 mg (Group D, n = 43). The incidence and severity of POST and hoarseness were evaluated at 1, 6 and 24 hours after surgery.
Results: Incidences and severities of POST at rest and during swallowing in first 6 hours after extubation were comparable among 4 groups. At 24 hours postextubation, the incidence (P = 0.002, 95% CI of proportion differences; 0.05-0.39) and severity (P = 0.008) of POST during swallowing were significantly lower in group D than in group C. Kpre and Kpost groups did not show a greater reduction in POST than group C, despite lower rescue analgesic requirement at 1 hour after extubation in group Kpre (P = 0.006; 95% CI of proportion differences; 0.07-0.38). No intergroup differences were observed in incidences of hoarseness or adverse events.
Conclusions: Intravenous administration of dexamethasone 10 mg, but not ketorolac, before induction of anesthesia reduces the incidence and severity of POST during swallowing at 24 hours after thyroidectomy.
Keywords: Dexamethasone; Hoarseness; Intubation; Ketorolac; Sore throat; Thyroidectomy.
References
-
- Ryu JH, Yom CK, Park DJ, Kim KH, Do SH, Yoo SH, et al. Prospective randomized controlled trial on the use of flexible reinforced laryngeal mask airway (LMA) during total thyroidectomy: effects on postoperative laryngopharyngeal symptoms. World J Surg. 2014;38:378–384. - PubMed
-
- Christensen AM, Willemoes-Larsen H, Lundby L, Jakobsen KB. Postoperative throat complaints after tracheal intubation. Br J Anaesth. 1994;73:786–787. - PubMed
-
- Xu YJ, Wang SL, Ren Y, Zhu Y, Tan ZM. A smaller endotracheal tube combined with intravenous lidocaine decreases post-operative sore throat - a randomized controlled trial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2012;56:1314–1320. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical