Reconstruction of ancestral RNA sequences under multiple structural constraints
- PMID: 28185557
- PMCID: PMC5123390
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-016-3105-4
Reconstruction of ancestral RNA sequences under multiple structural constraints
Abstract
Background: Secondary structures form the scaffold of multiple sequence alignment of non-coding RNA (ncRNA) families. An accurate reconstruction of ancestral ncRNAs must use this structural signal. However, the inference of ancestors of a single ncRNA family with a single consensus structure may bias the results towards sequences with high affinity to this structure, which are far from the true ancestors.
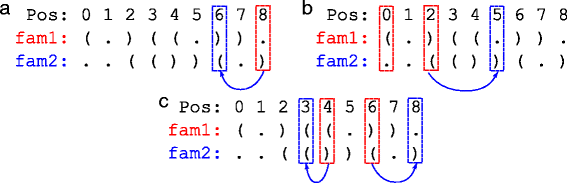
Methods: In this paper, we introduce achARNement, a maximum parsimony approach that, given two alignments of homologous ncRNA families with consensus secondary structures and a phylogenetic tree, simultaneously calculates ancestral RNA sequences for these two families.
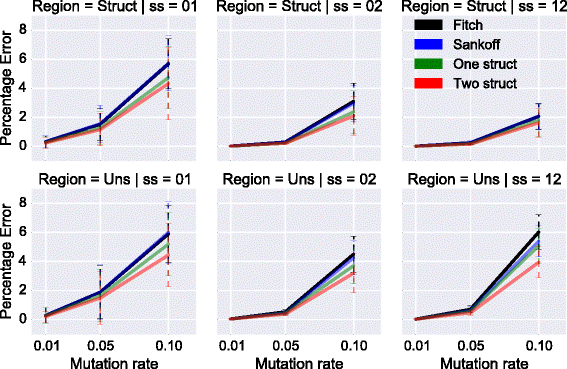
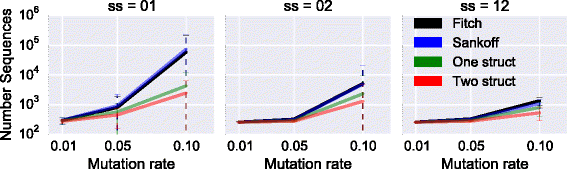
Results: We test our methodology on simulated data sets, and show that achARNement outperforms classical maximum parsimony approaches in terms of accuracy, but also reduces by several orders of magnitude the number of candidate sequences. To conclude this study, we apply our algorithms on the Glm clan and the FinP-traJ clan from the Rfam database.
Conclusions: Our results show that our methods reconstruct small sets of high-quality candidate ancestors with better agreement to the two target structures than with classical approaches. Our program is freely available at: http://csb.cs.mcgill.ca/acharnement .
Keywords: Algorithm; Ancestor reconstruction; Evolution; Phylogeny; RNA; Secondary structure.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Median and small parsimony problems on RNA trees.Bioinformatics. 2024 Jun 28;40(Suppl 1):i237-i246. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae229. Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 38940169 Free PMC article.
-
Rfam 11.0: 10 years of RNA families.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan;41(Database issue):D226-32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1005. Epub 2012 Nov 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23125362 Free PMC article.
-
Structural alignment of RNA with complex pseudoknot structure.J Comput Biol. 2011 Jan;18(1):97-108. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2009.0275. J Comput Biol. 2011. PMID: 21210732
-
Sequence and structure analysis of noncoding RNAs.Methods Mol Biol. 2010;609:285-306. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-241-4_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20221926 Review.
-
Computational methods in noncoding RNA research.J Math Biol. 2008 Jan;56(1-2):15-49. doi: 10.1007/s00285-007-0122-6. Epub 2007 Sep 4. J Math Biol. 2008. PMID: 17786447 Review.
Cited by
-
Median and small parsimony problems on RNA trees.Bioinformatics. 2024 Jun 28;40(Suppl 1):i237-i246. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae229. Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 38940169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pauling L, Zuckerkandl E. Chemical paleogenetics, molecular restoration studies of extinct forms of life. Acta Chem Scand. 1963;17(9-16):S9–16. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.17s-0009. - DOI
-
- Snir S, Pachter L. Phylogenetic profiling of insertions and deletions in vertebrate genomes. In: Research in Computational Molecular Biology, 10th Annual International Conference, RECOMB 2006, Venice, Italy, April 2-5, 2006, Proceedings: 2006. p. 265–80, doi:10.1007/11732990_23. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

