Var2GO: a web-based tool for gene variants selection
- PMID: 28185576
- PMCID: PMC5123234
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-016-1197-0
Var2GO: a web-based tool for gene variants selection
Abstract
Background: One of the most challenging issue in the variant calling process is handling the resulting data, and filtering the genes retaining only the ones strictly related to the topic of interest. Several tools permit to gather annotations at different levels of complexity for the detected genes and to group them according to the pathways and/or processes they belong to. However, it might be a time consuming and frustrating task. This is partly due to the size of the file, that might contain many thousands of genes, and to the search of associated variants that requires a gene-by-gene investigation and annotation approach. As a consequence, the initial gene list is often reduced exploiting the knowledge of variants effect, novelty and genotype, with the potential risk of losing meaningful pieces of information.
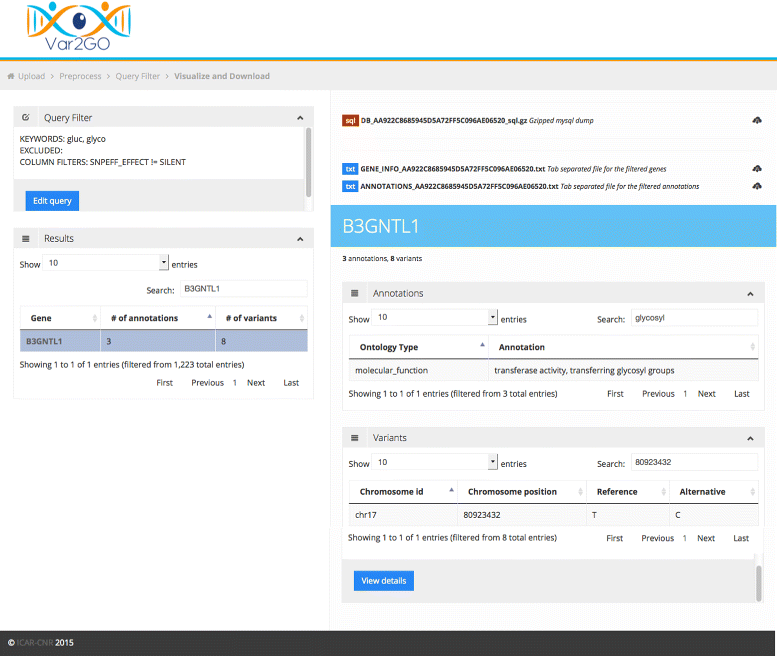
Results: Here we present Var2GO, a new web-based tool to support the annotation and filtering of variants and genes coming from variant calling of high-throughput sequencing data. Var2GO permits to upload either the unprocessed Variant Calling Format file or a table containing the annotated variants. The raw data undergo a preliminary step of variants annotation, using the SnpEff tool, and are converted to a table format. The table is then uploaded into an on the fly generated database. Genes associated to the variants are automatically annotated with the corresponding Gene Ontology terms covering the three GO domains. Using the web interface it is then possible to filter and extract, from the whole list, genes having annotations in the domain of interest, by simply specifying filtering parameters and one or more keywords. The relevance of this tool is demonstrated on exome sequencing data.
Conclusions: Var2GO is a novel tool that implements a topic-based approach, expressly designed to help biologists in narrowing the search of relevant genes coming from variant calling analysis. Its main purpose is to support non-bioinformaticians in handling and processing raw variant calling data through an intuitive web interface. Furthermore, Var2GO offers a complete pipeline that, starting from the raw VCF file, allows to annotate both variants and associated genes and supports the extraction of relevant biological knowledge.
Keywords: Annotation; Gene ontology; Gene variants; Next generation sequencing; Web-based tool.
Figures
References
-
- Cingolani P, Platts A, Wang LL, Coon M, Nguyen T, Wang L, Land SJ, Lu X, Ruden DM. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: Snps in the genome of drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly. 2012;6(2):80–92. doi: 10.4161/fly.19695. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

