STAT1 mediates transmembrane TNF-alpha-induced formation of death-inducing signaling complex and apoptotic signaling via TNFR1
- PMID: 28186502
- PMCID: PMC5384023
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2016.162
STAT1 mediates transmembrane TNF-alpha-induced formation of death-inducing signaling complex and apoptotic signaling via TNFR1
Abstract
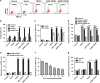
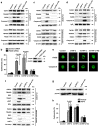
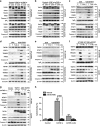
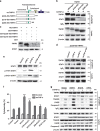
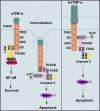
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) exists in two forms: secretory TNF-α (sTNF-α) and transmembrane TNF-α (tmTNF-α). Although both forms of TNF-α induce tumor cell apoptosis, tmTNF-α is able to kill tumor cells that are resistant to sTNF-α-mediated cytotoxicity, indicating their differences in signal transduction. Here, we demonstrate that internalization of TNFR1 is crucial for sTNF-α- but not for tmTNF-α-induced apoptosis. sTNF-α induces binding of tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1-associated death domain protein (TRADD) to the death domain (DD) of TNFR1 and subsequent activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), and the formation of death-inducing signaling complexes (DISCs) in the cytoplasm after internalization. In contrast, tmTNF-α induces DISC formation on the membrane in a DD-independent manner. It leads to the binding of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) to a region spanning amino acids 319-337 of TNFR1 and induces phosphorylation of serine at 727 of STAT1. The phosphorylation of STAT1 promotes its binding to TRADD, and thus recruits Fas-associated protein with DD (FADD) and caspase 8 to form DISC complexes. This STAT1-dependent signaling results in apoptosis but not NF-κB activation. STAT1-deficiency in U3A cells counteracts tmTNF-α-induced DISC formation and apoptosis. Conversely, reconstitution of STAT1 expression restores tmTNF-α-induced apoptotic signaling in the cell line. Consistently, tmTNF-α suppresses the growth of STAT1-containing HT1080 tumors, but not of STAT1-deficient U3A tumors in vivo. Our data reveal an unappreciated molecular mechanism of tmTNF-α-induced apoptosis and may provide a new clue for cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kriegler M, Perez C, DeFay K, Albert I, Lu SD. A novel form of TNF/cachectin is a cell surface cytotoxic transmembrane protein: ramifications for the complex physiology of TNF. Cell 1988; 53: 45–53. - PubMed
-
- Black RA, Rauch CT, Kozlosky CJ, Peschon JJ, Slack JL, Wolfson MF et al. A metalloproteinase disintegrin that releases tumour-necrosis factor-alpha from cells. Nature 1997; 385: 729–733. - PubMed
-
- Grell M, Douni E, Wajant H, Lohden M, Clauss M, Maxeiner B et al. The transmembrane form of tumor necrosis factor is the prime activating ligand of the 80 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell 1995; 83: 793–802. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

