An oral quinoline derivative, MPT0B392, causes leukemic cells mitotic arrest and overcomes drug resistant cancer cells
- PMID: 28186963
- PMCID: PMC5438607
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15115
An oral quinoline derivative, MPT0B392, causes leukemic cells mitotic arrest and overcomes drug resistant cancer cells
Abstract
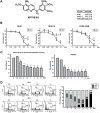
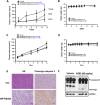
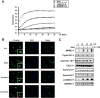
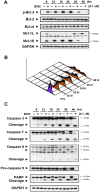
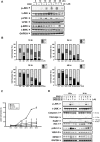
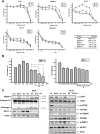
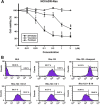
Despite great advances in the treatment of acute leukemia, a renaissance of current chemotherapy needs to be improved. The present study elucidates the underlying mechanism of a new synthetic quinoline derivative, MPT0B392 (B392) against acute leukemia and its potential anticancer effect in drug resistant cells. B392 caused mitotic arrest and ultimately led to apoptosis. It was further demonstrated to be a novel microtubule-depolymerizing agent. The effects of oral administration of B392 showed relative potent anti-leukemia activity in an in vivo xenograft model. Further investigation revealed that B392 triggered induction of the mitotic arrest, followed by mitochondrial membrane potential loss and caspases cleavage by activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). In addition, B392 enhanced the cytotoxicity of sirolimus in sirolimus-resistant acute leukemic cells through inhibition of Akt/mTOR pathway and Mcl-1 protein expression, and also was active in the p-glycoprotein (p-gp)-overexpressing National Cancer Institute/Adriamycin-Resistant cells with little susceptibility to p-gp. Taken together, B392 has potential as an oral mitotic drug and adjunct treatment for drug resistant cancer cells.
Keywords: MPT0B392; acute leukemia; drug resistance; mitotic arrest.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no competing interests in this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro and in vivo anti-tumour effects of MPT0B014, a novel derivative aroylquinoline, and in combination with erlotinib in human non-small-cell lung cancer cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Jan;171(1):122-33. doi: 10.1111/bph.12427. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24116948 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Glucocorticoid Resistance in Pediatric T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia by Increasing BIM Expression with the PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor BEZ235.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Feb 1;22(3):621-32. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0114. Epub 2015 Jun 16. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26080839 Free PMC article.
-
3,3'-Diindolylmethane exhibits antileukemic activity in vitro and in vivo through a Akt-dependent process.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31783. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031783. Epub 2012 Feb 21. PLoS One. 2012. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2020 Feb 6;15(2):e0229164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229164. PMID: 22363731 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The cytoskeleton as a therapeutic target in childhood acute leukemia: obstacles and opportunities.Curr Drug Targets. 2007 Jun;8(6):739-49. doi: 10.2174/138945007780830836. Curr Drug Targets. 2007. PMID: 17584029 Review.
-
Apoptotic effects of chrysin in human cancer cell lines.Int J Mol Sci. 2010 May 19;11(5):2188-99. doi: 10.3390/ijms11052188. Int J Mol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20559509 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel insights on [1,2]oxazolo[5,4-e]isoindoles on multidrug resistant acute myeloid leukemia cell line.Drug Dev Res. 2022 Sep;83(6):1331-1341. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21962. Epub 2022 Jun 24. Drug Dev Res. 2022. PMID: 35749723 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrahydroquinolinone derivatives exert antiproliferative effect on lung cancer cells through apoptosis induction.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 9;12(1):19076. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23640-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36352170 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Methylselenoesters as Antiproliferative Agents.Molecules. 2017 Aug 2;22(8):1288. doi: 10.3390/molecules22081288. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28767087 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

