Inhibiting DNA-PKcs in a non-homologous end-joining pathway in response to DNA double-strand breaks
- PMID: 28186989
- PMCID: PMC5410253
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15153
Inhibiting DNA-PKcs in a non-homologous end-joining pathway in response to DNA double-strand breaks
Abstract
DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) is a distinct factor in the non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) pathway involved in DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair. We examined the crosstalk between key proteins in the DSB NHEJ repair pathway and cell cycle regulation and found that mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) cells deficient in DNA-PKcs or Ku70 were more vulnerable to ionizing radiation (IR) compared with wild-type cells and that DSB repair was delayed. γH2AX was associated with phospho-Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated kinase (Ser1987) and phospho-checkpoint effector kinase 1 (Ser345) foci for the arrest of cell cycle through the G2/M phase. Inhibition of DNA-PKcs prolonged IR-induced G2/M phase arrest because of sequential activation of cell cycle checkpoints. DSBs were introduced, and cell cycle checkpoints were recruited after exposure to IR in nasopharyngeal carcinoma SUNE-1 cells. NU7441 radiosensitized MEF cells and SUNE-1 cells by interfering with DSB repair. Together, these results reveal a mechanism in which coupling of DSB repair with the cell cycle radiosensitizes NHEJ repair-deficient cells, justifying further development of DNA-PK inhibitors in cancer therapy.
Keywords: DNA-PKcs; NU7441; double-strand break; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; non-homologous end-joining.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

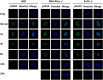
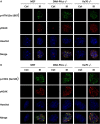

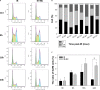


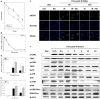
References
-
- Felgentreff K, Du L, Weinacht KG, Dobbs K, Bartish M, Giliani S, Schlaeger T, DeVine A, Schambach A, Woodbine LJ, Davies G, Baxi SN, van der Burg M, et al. Differential role of nonhomologous end joining factors in the generation, DNA damage response, and myeloid differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:8889–8894. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Curtin NJ. DNA repair dysregulation from cancer driver to therapeutic target. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:801–817. - PubMed
-
- Foulkes WD, Shuen AY. brief: BRCA1 and BRCA2. J Pathol. 2013;230:347–349. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

