Kidney Organoids: A Translational Journey
- PMID: 28188103
- PMCID: PMC5442988
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2017.01.001
Kidney Organoids: A Translational Journey
Abstract
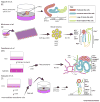
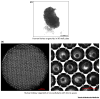
Human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) are attractive sources for regenerative medicine and disease modeling in vitro. Directed hPSC differentiation approaches have derived from knowledge of cell development in vivo rather than from stochastic cell differentiation. Moreover, there has been great success in the generation of 3D organ-buds termed 'organoids' from hPSCs; these consist of a variety of cell types in vitro that mimic organs in vivo. The organoid bears great potential in the study of human diseases in vitro, especially when combined with CRISPR/Cas9-based genome-editing. We summarize the current literature describing organoid studies with a special focus on kidney organoids, and discuss goals and future opportunities for organoid-based studies.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
J.V.B. is a co-inventor on KIM-1 patents that have been licensed by Partners Healthcare to several companies. He has received royalty income from Partners Healthcare. J.V.B. and R.M. are co-inventors on patents (PCT/US16/52350) on organoid technologies that are assigned to Partners Healthcare. J.V.B. or his family has received income for consulting from companies interested in biomarkers: Sekisui, Millennium, Johnson & Johnson and Novartis. J.V.B. is a co-founder, consultant to, and owns equity in, Goldfinch Bio.
Figures
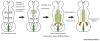

References
-
- Thomson JA, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282:1145–1147. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007;131:861–872. - PubMed
-
- Takasato M, et al. Directing human embryonic stem cell differentiation towards a renal lineage generates a self-organizing kidney. Nature cell biology. 2014;16:118–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

