Elevated Rate of Genome Rearrangements in Radiation-Resistant Bacteria
- PMID: 28188144
- PMCID: PMC5378121
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.116.196154
Elevated Rate of Genome Rearrangements in Radiation-Resistant Bacteria
Abstract
A number of bacterial, archaeal, and eukaryotic species are known for their resistance to ionizing radiation. One of the challenges these species face is a potent environmental source of DNA double-strand breaks, potential drivers of genome structure evolution. Efficient and accurate DNA double-strand break repair systems have been demonstrated in several unrelated radiation-resistant species and are putative adaptations to the DNA damaging environment. Such adaptations are expected to compensate for the genome-destabilizing effect of environmental DNA damage and may be expected to result in a more conserved gene order in radiation-resistant species. However, here we show that rates of genome rearrangements, measured as loss of gene order conservation with time, are higher in radiation-resistant species in multiple, phylogenetically independent groups of bacteria. Comparison of indicators of selection for genome organization between radiation-resistant and phylogenetically matched, nonresistant species argues against tolerance to disruption of genome structure as a strategy for radiation resistance. Interestingly, an important mechanism affecting genome rearrangements in prokaryotes, the symmetrical inversions around the origin of DNA replication, shapes genome structure of both radiation-resistant and nonresistant species. In conclusion, the opposing effects of environmental DNA damage and DNA repair result in elevated rates of genome rearrangements in radiation-resistant bacteria.
Keywords: Deinococcus radiodurans; gamma radiation; gene order; genome stability; synteny.
Copyright © 2017 Repar et al.
Figures
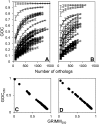

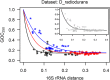
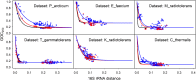

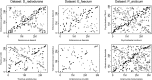
References
-
- Abomohra A. E.-F., El-Shouny W., Sharaf M., Abo-Eleneen M., 2016. Effect of gamma radiation on growth and metabolic activities of Arthrospira platensis. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 59: e16150476.
-
- Achaz G., Boyer F., Rocha E. P. C., Viari A., Coissac E., 2007. Repseek, a tool to retrieve approximate repeats from large DNA sequences. Bioinformatics 23: 119–121. - PubMed
-
- Albuquerque L., Simoes C., Nobre M. F., Pino N. M., Battista J. R., et al. , 2005. Truepera radiovictrix gen. nov., sp. nov., a new radiation resistant species and the proposal of Trueperaceae fam. nov. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 247: 161–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

