Hypoxic proliferation requires EGFR-mediated ERK activation in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 28188223
- PMCID: PMC6148326
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00267.2016
Hypoxic proliferation requires EGFR-mediated ERK activation in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells
Abstract
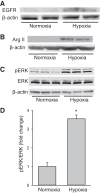
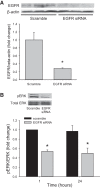
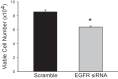
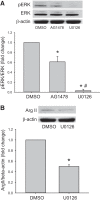
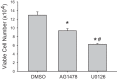
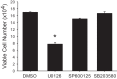
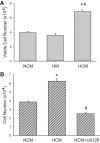
We have previously shown that hypoxic proliferation of human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (hPMVECs) depends on epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) activation. To determine downstream signaling leading to proliferation, we tested the hypothesis that hypoxia-induced proliferation in hPMVECs would require EGFR-mediated activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) leading to arginase II induction. To test this hypothesis, hPMVECs were incubated in either normoxia (21% O2, 5% CO2) or hypoxia (1% O2, 5% CO2) and Western blotting was performed for EGFR, arginase II, phosphorylated-ERK (pERK), and total ERK (ERK). Hypoxia led to greater EGFR, pERK, and arginase II protein levels than did normoxia in hPMVECs. To examine the role of EGFR in these hypoxia-induced changes, hPMVECs were transfected with siRNA against EGFR or a scrambled siRNA and placed in hypoxia. Inhibition of EGFR using siRNA attenuated hypoxia-induced pERK and arginase II expression as well as the hypoxia-induced increase in viable cell numbers. hPMVECs were then treated with vehicle, an EGFR inhibitor (AG1478), or an ERK pathway inhibitor (U0126) and placed in hypoxia. Pharmacologic inhibition of EGFR significantly attenuated the hypoxia-induced increase in pERK level. Both AG1478 and U0126 also significantly attenuated the hypoxia-induced increase in viable hPMVECs numbers. hPMVECs were transfected with an adenoviral vector containing arginase II (AdArg2) and overexpression of arginase II rescued the U0126-mediated decrease in viable cell numbers in hypoxic hPMVECs. Our findings suggest that hypoxic activation of EGFR results in phosphorylation of ERK, which is required for hypoxic induction of arginase II and cellular proliferation.
Keywords: arginase; hypoxia; pulmonary hypertension; pulmonary vascular remodeling.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hypoxic-induction of arginase II requires EGF-mediated EGFR activation in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells.Physiol Rep. 2018 May;6(10):e13693. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13693. Physiol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29845760 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-induced proliferation of human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells depends on epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase activation.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010 Apr;298(4):L600-6. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00122.2009. Epub 2010 Feb 5. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20139181 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-induced proliferation of HeLa cells depends on epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated arginase II induction.Physiol Rep. 2017 Mar;5(6):e13175. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13175. Physiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28330951 Free PMC article.
-
From epithelial remodelling to carcinogenesis.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2020 Jan;150:203-205. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2019.08.001. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31381892 Review.
-
HTS for Identification of Inhibitors against the ERK Signaling Pathway using a Homogenous Cell-based Assay.2009 May 18 [updated 2010 Sep 2]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. 2009 May 18 [updated 2010 Sep 2]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. PMID: 21433365 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channel openers diazoxide and nicorandil lower intraocular pressure by activating the Erk1/2 signaling pathway.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 8;12(6):e0179345. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179345. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28594895 Free PMC article.
-
DDAH1 regulates apoptosis and angiogenesis in human fetal pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells.Physiol Rep. 2019 Jul;7(12):e14150. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14150. Physiol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31209995 Free PMC article.
-
Human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell DDAH1-mediated nitric oxide production promotes pulmonary smooth muscle cell apoptosis in co-culture.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2023 Sep 1;325(3):L360-L367. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00433.2021. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37431589 Free PMC article.
-
The P2-receptor-mediated Ca2+ signalosome of the human pulmonary endothelium - implications for pulmonary arterial hypertension.Purinergic Signal. 2019 Sep;15(3):299-311. doi: 10.1007/s11302-019-09674-1. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Purinergic Signal. 2019. PMID: 31396838 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxic-induction of arginase II requires EGF-mediated EGFR activation in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells.Physiol Rep. 2018 May;6(10):e13693. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13693. Physiol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29845760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chicoine LG, Stenger MR, Cui H, Calvert A, Evans RJ, English BK, Liu Y, Nelin LD. Nitric oxide suppression of cellular proliferation depends on cationic amino acid transporter activity in cytokine-stimulated pulmonary endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol : L596–L604, 2011. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00029.2010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

