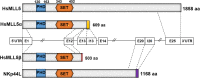
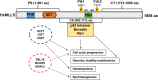
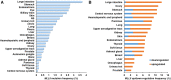
MLL5 (KMT2E): structure, function, and clinical relevance
- PMID: 28188343
- PMCID: PMC11107642
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-017-2470-8
MLL5 (KMT2E): structure, function, and clinical relevance
Abstract
The mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) family of genes, also known as the lysine N-methyltransferase 2 (KMT2) family, are homologous to the evolutionarily conserved trithorax group that plays critical roles in the regulation of homeotic gene (HOX) expression and embryonic development. MLL5, assigned as KMT2E on the basis of its SET domain homology, was initially categorized under MLL (KMT2) family together with other six SET methyltransferase domain proteins (KMT2A-2D and 2F-2G). However, emerging evidence suggests that MLL5 is distinct from the other MLL (KMT2) family members, and the protein it encodes appears to lack intrinsic histone methyltransferase (HMT) activity towards histone substrates. MLL5 has been reported to play key roles in diverse biological processes, including cell cycle progression, genomic stability maintenance, adult hematopoiesis, and spermatogenesis. Recent studies of MLL5 variants and isoforms and putative MLL5 homologs in other species have enriched our understanding of the role of MLL5 in gene expression regulation, although the mechanism of action and physiological function of MLL5 remains poorly understood. In this review, we summarize recent research characterizing the structural features and biological roles of MLL5, and we highlight the potential implications of MLL5 dysfunction in human disease.
Keywords: Cancer; Cell division; Hematopoietic stem cell differentiation; Histone methylation; Leukemia; PHD finger.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kratz CP, Emerling BM, Donovan S, Laig-Webster M, Taylor BR, Thompson P, Jensen S, Banerjee A, Bonifas J, Makalowski W. Candidate gene isolation and comparative analysis of a commonly deleted segment of 7q22 implicated in myeloid malignancies. Genomics. 2001;77(3):171–180. doi: 10.1006/geno.2001.6636. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Madan V, Madan B, Brykczynska U, Zilbermann F, Hogeveen K, Döhner K, Döhner H, Weber O, Blum C, Rodewald HR, Sassone-Corsi P, Peters AH, Fehling HJ. Impaired function of primitive hematopoietic cells in mice lacking the Mixed-Lineage-Leukemia homolog MLL5. Blood. 2009;113(7):1444–1454. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-02-142638. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mas-y-Mas S, Barbon M, Teyssier C, Déméné H, Carvalho JE, Bird LE, Lebedev A, Fattori J, Schubert M, Dumas C, Bourguet W, le Maire A. The human mixed lineage leukemia 5 (MLL5), a sequentially and structurally divergent SET domain-containing protein with no intrinsic catalytic activity. PLos One. 2016;11(11):e0165139. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165139. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

