Hepatitis B immunoglobulin during pregnancy for prevention of mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B virus
- PMID: 28188612
- PMCID: PMC6464495
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008545.pub2
Hepatitis B immunoglobulin during pregnancy for prevention of mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B virus
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis is a viral infection of the liver. It is mainly transmitted between people through contact with infected blood, frequently from mother to baby in-utero. Hepatitis B poses significant risk to the fetus and up to 85% of infants infected by their mothers at birth develop chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIG) is a purified solution of human immunoglobulin that could be administered to the mother, newborn, or both. HBIG offers protection against HBV infection when administered to pregnant women who test positive for hepatitis B envelope antigen (HBeAg) or hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), or both. When HBIG is administered to pregnant women, the antibodies passively diffuse across the placenta to the child. This materno-fetal diffusion is maximal during the third trimester of pregnancy. Up to 1% to 9% infants born to HBV-carrying mothers still have HBV infection despite the newborn receiving HBIG plus active HBV vaccine in the immediate neonatal period. This suggests that additional intervention such as HBIG administration to the mother during the antenatal period could be beneficial to reduce the transmission rate in utero.
Objectives: To determine the benefits and harms of hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIG) administration to pregnant women during their third trimester of pregnancy for the prevention of mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B virus infection.
Search methods: We searched the The Cochrane Hepato-Biliary Group Controlled Trials Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE Ovid, Embase Ovid, Science Citation Index Expanded (Web of Science), SCOPUS, African Journals OnLine, and INDEX MEDICUS up to June 2016. We searched ClinicalTrials.gov and portal of the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) in December 2016.
Selection criteria: We included randomised clinical trials comparing HBIG versus placebo or no intervention in pregnant women with HBV.
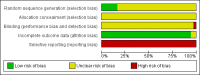
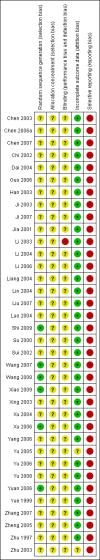
Data collection and analysis: Two authors extracted data independently. We analysed dichotomous outcome data using risk ratio (RR) and continuous outcome data using mean difference (MD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). For meta-analyses, we used a fixed-effect model and a random-effects model, along with an assessment of heterogeneity. If there were statistically significant discrepancies in the results, we reported the more conservative point estimate. If the two estimates were equal, we used the estimate with the widest CI as our main result. We assessed bias control using the Cochrane Hepato-Biliary Group suggested bias risk domains and risk of random errors using Trial Sequential Analysis (TSA). We assessed the quality of the evidence using GRADE.
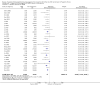
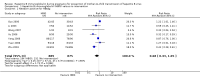
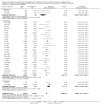
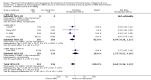
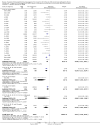
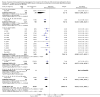
Main results: All 36 included trials originated from China and were at overall high risk of bias. The trials included 6044 pregnant women who were HBsAg, HBeAg, or hepatitis B virus DNA (HBV-DNA) positive. Only seven trials reported inclusion of HBeAg-positive mothers. All 36 trials compared HBIG versus no intervention. None of the trials used placebo.Most of the trials assessed HBIG 100 IU (two trials) and HBIG 200 IU (31 trials). The timing of administration of HBIG varied; 30 trials administered three doses of HBIG 200 IU at 28, 32, and 36 weeks of pregnancy. None of the trials reported all-cause mortality or other serious adverse events in the mothers or babies. Serological signs of hepatitis B infection of the newborns were reported as HBsAg, HBeAg, and HBV-DNA positive results at end of follow-up. Twenty-nine trials reported HBsAg status in newborns (median 1.2 months of follow-up after birth; range 0 to 12 months); seven trials reported HBeAg status (median 1.1 months of follow-up after birth; range 0 to 12 months); and 16 trials reported HBV-DNA status (median 1.2 months of follow-up; range 0 to 12 months). HBIG reduced mother-to-child transmission (MTCT) of HBsAg when compared with no intervention (179/2769 (6%) with HBIG versus 537/2541 (21%) with no intervention; RR 0.30, TSA-adjusted CI 0.20 to 0.52; I2 = 36%; 29 trials; 5310 participants; very low quality evidence). HBV-DNA reduced MTCT of HBsAg (104/1112 (9%) with HBV-DNA versus 382/1018 (38%) with no intervention; RR 0.25, TSA-adjusted CI 0.22 to 0.27; I2 = 84%; 16 trials; 2130 participants; low quality evidence). TSA supported both results. Meta-analysis showed that maternal HBIG did not decrease HBeAg in newborns compared with no intervention (184/889 (21%) with HBIG versus 232/875 (27%) with no intervention; RR 0.68, TSA-adjusted CI 0.04 to 6.37; I2 = 90%; 7 trials; 1764 participants; very low quality evidence). TSA could neither support nor refute this observation as data were too sparse. None of the trials reported adverse events of the immunoglobulins on the newborns, presence of local and systemic adverse events on the mothers, or cost-effectiveness of treatment.
Authors' conclusions: Due to very low to low quality evidence found in this review, we are uncertain of the effect of benefit of antenatal HBIG administration to the HBV-infected mothers on newborn outcomes, such as HBsAg, HBV-DNA, and HBeAg compared with no intervention. The results of the effects of HBIG on HBsAg and HBeAg are surrogate outcomes (raising risk of indirectness), and we need to be critical while interpreting the findings. We found no data on newborn mortality or maternal mortality or both, or other serious adverse events. Well-designed randomised clinical trials are needed to determine the benefits and harms of HBIG versus placebo in prevention of MTCT of HBV.
Conflict of interest statement
ACE: no conflict of interest GUE: no conflict of interest UAE: no conflict of interest YX: no conflict of interest JL: no conflict of interest
Figures
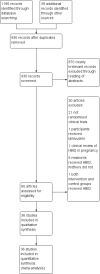



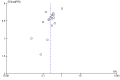



Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Chen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Chen XY, Luo ZY, Xuan ZB, Yu LP. Study on immunoglobulin of hepatitis B in stopping transmission from mother to infant. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 2003;15(7):10‐1.
Chen 2006a {published data only}
-
- Chen QM, Chen W. The clinical observation on the effect of hepatitis B immunoglobulin on the interruption of hepatitis B virus intrauterine infection. Hebei Medicine 2006;12(6):534‐6.
Chen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Chen WL, Lu CS, Lai LP. Observation on the results of HBIG combined with hepatitis B vaccine interruption of vertical transmission of HBV. China Tropical Medicine 2007;7(7):1177‐8.
Chi 2002 {published data only}
-
- Chi MZ, Wang YY, Shuai CX. Clinical study of prenatal injection of HBIG in prevention of HBV intrauterine infectious. Chinese Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics 2002;4(2):127‐8.
Dai 2004 {published data only}
-
- Dai XJ. 86 cases of HBIG in prevention of hepatitis B virus intrauterine infectious. Herald of Medicine 2004;23(8):535.
Guo 2006 {published data only}
-
- Guo SH, Wang JL, Song YL. Observation of effect of hepatitis B vaccine single use and combination use with HBIG in blocking HBV mother‐infant transmission. Journal of Medicinal Forum 2006;27(3):10‐3.
Han 2003 {published data only}
-
- Han GR, Yu MM, Shen L, Tang X, Wu MM, Zhang XY, et al. The clinical effect evaluation of HBIG blocking intrauterine infectious of HBV. Jiangsu Medical Journal 2003;29(11):833‐5.
Ji 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ji LD. Clinical report of HBIG in interruption of hepatitis B intrauterine infectious. Modern Preventive Medicine 2003;30(3):380‐1.
Ji 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ji XH. Observation of HBIG in interruption mother to child transmission of HBV. Shanghai Journal of Preventive Medicine 2007;19(5):217.
Jia 2001 {published data only}
-
- Jia QQ, Gu Y. The blocking effect of hepatitis B immunoglobulin on HBV intrauterine infection and its indication. Chinese Journal of Neonatology 2001;16(5):196‐7.
Li 2003 {published and unpublished data}
Li 2004 {published and unpublished data}
Li 2006 {published data only}
-
- Li H, Song XJ. Study on the use of HBIG to prevent mother to child HBV transmission. Journal of Mathematical Medicine 2006;19(1):42‐3.
Liang 2004 {published data only}
-
- Liang BZ. Study about intrauterine hepatitis B virus infection and clinical application of HBIg during pregnant period. Maternal and Child Health Care of China 2004;19(2):81‐3.
Lin 2004 {published data only}
-
- Lin HT, Liang AL, Li M. Effect of hepatitis B immunoglobulin combining with hepatitis B vaccine in interrupting maternal‐fetal transmission of hepatitis B virus. Chinese Medical Journal 2004;5:486‐7.
Liu 2007 {published data only}
-
- Liu JY, Lu GR. Comparison of efficiency of two methods in preventing HBV maternal fetal transmission. Clinical Medicine 2007;27(10):13‐4.
Luo 2004 {published data only}
-
- Luo HF, Han WL, Leng LL, Tang BZ. Clinical study of HBIG passive immunization of pregnant women in interruption mother to child transmission of HBV. Journal of Gannan Medical College 2004;24(3):270‐2.
Shi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Shi ZJ, Li XM, Yang YB, Ma L. Clinical research on the interruption of mother to child transmission of HBV ‐ a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. 6th Annual Global Health Conference; 2009 Apr 18‐19; New Haven (CT): Yale University. 2009.
Su 2000 {published data only}
-
- Su ZJ, Li H, Zhang T. Clinical study of the efficacy of hepatitis B immunoglobulin in the interruption of the intrauterine transmission with hepatitis B virus. Chinese Journal of Medical Laboratory Technology 2000;1(2):98‐101.
Sui 2002 {published data only}
-
- Sui LY, Gao YJ. Clinical analysis of HBIG intramuscular injection of pregnant women in prevention of hepatitis B virus intrauterine infection. Chinese Journal of Family Planning 2002;5:290‐1.
Wang 2007 {published data only}
-
- Wang YL, Lv SF. A clinical study of interruptive effects of HBV specific immunoglobulins on the HBsAg + and HBeAg + women in midtrimester pregnancy. Medical Journal of Qilu 2007;22:154‐5.
Wang 2008 {published data only}
-
- Wang FY, Lin P, Zhang HZ. A randomized controlled trial on effect of hepatitis B immune globulin in preventing hepatitis B virus transmission from mothers to infants. Chinese Journal of Pediatrics 2008;46(1):61‐3. [PUBMED: 18353242] - PubMed
Xiao 2009 {published data only}
-
- Xiao L, Xu Q, Lu XB, Zhang YX, Cai X. Effect of hepatitis B immunoglobulin on interruption of HBV intrauterine infection. Hepatology International Conference: 19th Conference of the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver; 2009 Feb 13‐16; Hong Kong, China. 2009.
Xing 2003 {published data only}
-
- Xing QX, Yue F, Zhang CH, Zong XY, Li ZZ, Wang JJ, et al. Clinical study of prenatal administration of HBIG in interruption intrauterine infection of hepatitis B virus. Journal of Applied Clinical Pediatrics 2003;18(4):283‐5.
Xu 2004 {published data only}
-
- Xu L, Ye YH, Wang Y, Peng W. Effects of HBIG on the prevention of HBV vertical transmission from gravidas to infants. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 2004;40(3):246‐8.
Xu 2006 {published and unpublished data}
Yang 2006 {published data only}
-
- Yang LT, Nie Y. The influence of prenatal immunization in interruption of HBV intrauterine infectious. Chinese Journal of Current Practical Medicine 2006;5(9):9‐10.
Yu 2005 {published data only}
-
- Yu F, Lin J. Clinical analysis of HBIG in prevention of HBV infectious of mother to child in 60 cases. Maternal and Child Health Care of China 2005;20(10):1272‐3.
Yu 2006 {published data only}
-
- Yu H, Zhu QR, Chen SQ, Xie XB, Chen H, Wang JS, et al. Study on a antepartum immunoprophylaxis to interrupt the transmission of hepatitis B virus from mother to infant. Chinese Journal of Infectious Disease 2006;24(6):390‐1.
Yu 2008 {published data only}
-
- Yu JY, Wang Y. Clinical application of HBIG in prevention of intrauterine infectious of HBV. Journal of Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities 2008;1:87‐8.
Yuan 2006 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Yuan J, Lin J, Xu A, Li H, Hu B, Chen J, et al. Antepartum immunoprophylaxis of three doses of hepatitis B immunoglobulin is not effective: a single‐centre randomised study. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 2006;13:597‐604. - PubMed
Yue 1999 {published data only}
-
- Yue YF, Yang XJ, Zhang SL. Prevention of intrauterine infection by hepatitis B virus with hepatitis B immune globulin efficacy and mechanism. Chinese Medical Journal 1999;112(1):37‐9. - PubMed
Zhang 2007 {published data only}
-
- Zhang XL, Huang CH, Cheng HQ, Xie WJ. Study of hepatitis B virus and mother‐to‐child transmission. Chinese Journal of Postgraduates of Medicine 2007;30(8):41‐2.
Zheng 2005 {published data only}
-
- Zheng DY, Chen WY, Kuang RF, Liang YM. Clinical study of third trimester use of HBIG in interruption intrauterine infection. Journal of Practical Medicine 2005;21(12):1344‐5.
Zhu 1997 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Zhu Q, Lu Q, Gu X, Xu H, Duan S. A preliminary study on interruption of HBV transmission in uterus. Chinese Medical Journal 1997;110(2):145‐7. - PubMed
Zhu 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zhu Q, Yu G, Yu H, Lu Q, Gu X, Dong Z, et al. A randomized control trial on interruption of HBV transmission in uterus. Chinese Medical Journal 2003;116(5):685‐7. [PUBMED: 12875680] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Batham 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Batham A, Narula D, Toteja T, Sreenivas V, Puliyel M. Systematic review and meta‐analysis of prevalence of hepatitis B in India. Indian Journal of Paediatrics 2007;44(9):663‐74. - PubMed
Beasley 1981 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Beasley PR, Lin CC, Wang KY, Hwang LY, Stevens CE, Sun TS. Hepatitis B immune globulin efficacy in the interruption of hepatitis B virus carrier state. Lancet 1981;8:388‐93. - PubMed
Beasley 1983a {published and unpublished data}
-
- Beasley PR, Lin CC, Hwang LY, Stevens CE, Hsieh FJ, Wang KY. Efficacy of hepatitis B immune globulin for prevention of perinatal transmission of the hepatitis B carrier state: final report of a randomised double‐blind placebo controlled trial. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 1983;3(2):135‐41. - PubMed
Beasley 1983b {published and unpublished data}
-
- Beasley PR, Hwang LY, Lee GC, Lan CC, Huang FY, Raon CH. Prevention of perinatally transmitted hepatitis B virus infections with hepatitis B immune globulin and hepatitis B vaccine. Lancet 1983;12:1099‐102. - PubMed
Birnbaum 1992 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Birnbaum JM, Bromberg K. Evaluation of prophylaxis against hepatitis B in a large municipal hospital. American Journal of Infectious Control 1992;20(4):172‐6. - PubMed
Boisier 1996 {published and unpublished data}
Boutin 1990 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Boutin JP, Marie FS, Cartel JL, Cardines R, Girard M, Roux J. Prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection in the Austral archipelago, French Polynesia: identification of transmission patterns for the formulation of immunisation strategies. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1990;84:283‐7. - PubMed
Chen 2006b {published and unpublished data}
-
- Chen LM. A clinical study on the effect of anti‐HBV Ig on intrauterine HBV infection. Journal of Tropical Medicine 2006;6(3):306‐8.
Chung 1985 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Chung WK, Yoo JY, Sun HS, Lee HY, Lee IJ, Kim S, et al. Prevention of perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus: a comparison between the efficacy of passive and passive‐active immunization in Korea. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1985;151(2):280‐6. - PubMed
Da Conceicao 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Conceicao JS, Diniz‐Santos RD, Ferreira CD, Nunes FP, Nunes CM, Silva LR. Knowledge of obstetricians about the vertical transmission of hepatitis B virus. Archives of Gastroenterology 2009;46(1):57‐61. - PubMed
Denis 2004 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Denis F, Ranger‐Rogez S, Alain S, Mounier M, Debrock C, Wagner A. Screening of pregnant women for hepatitis B markers in a French provincial university hospital (Limoges) during 15 years. European Journal of Epidemiology 2004;19:973‐8. - PubMed
De Ruiter 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ruiter A, Mercey D, Anderson J, Chakraborty R, Clayden P, Foster G, et al. British HIV association and children's HIV association guidelines for the management of HIV infection in pregnant women. HIV Medicine 2008;9:452‐502. - PubMed
Edmunds 1996 {published and unpublished data}
Erdem 1994 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Erdem I, Tekinalp G, Yurdak M, Ozsoylu S, Kanra T, Durukan T. Perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 1994;343:289. - PubMed
Esteban 1986 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Esteban JI, Genesca J, Esteban R, Hernandez J, Seljo G, Buti M, et al. Immunoprophylaxis of perinatal transmission of the hepatitis B virus. Journal of Medical Virology 1986;18:381‐91. - PubMed
Euler 2003 {published and unpublished data}
Goudeau 1983 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Goudeau A, Lo KJ, Corsegej P, Tong MJ, Yeh CJ, Tsai YT, et al. Prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in children born to HBsAg positive/HBeAg mothers. Preliminary results of active and passive‐passive immunisation. Developments in Biological Standardisation 1983;54:399‐404. - PubMed
Gupta 2003 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Gupta I, Ratho RK. Immunogenicity and safety of two schedules of hepatitis B vaccination during pregnancy. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research 2003;29(2):84‐6. - PubMed
Harold 1995 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Harold MS, Coleman PJ, Brown RE, Mast EE, Sheingold SH, Arevalo JA. Prevention of hepatitis B virus infection by immunisation. Journal of the American Medical Association 1995;274(15):1201‐8. - PubMed
Jonas 2009 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Jonas MM. Hepatitis B and pregnancy: an underestimated issue. Liver International 2009;29(1):133‐9. - PubMed
Lo 1985 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Lo KJ, Tsai YT, Lee SD, Yoh CL, Wang JY, Chiang BN, et al. Combined active and passive immunisation for interruption of perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus in Taiwan. Hepato‐Gastroenterology 1985;32:65‐8. - PubMed
Nair 1984 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Nair PV, Weissman JY, Tong MJ, Thursby MW, Paul RH, Henneman CE. Efficacy of hepatitis B immune globulin in prevention of perinatal transmission of the hepatitis B virus. Gastroenterology 1984;87:293‐8. - PubMed
Pan 2006 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Pan JY, Zhong WP, Yan SL, Guo XJ, Fang Q, Shen XY. Study on anti‐HBV immunoglobulin in preventing intrauterine infection of HBV. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2006;5(1):12‐3.
Theppisai 1987 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Theppisai U, Chiewsilp P, Thanuntaseth C, Siripoonya P. A comparison between the efficacy of active‐passive and active immunisation for the prevention of perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 1987;70(8):458‐62. - PubMed
Tsega 1988 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Tsega E, Tsega M, Mengesha B, Nordenfel E, Hansson BG, Lingberg J. Transmission of hepatitis B virus infection in Ethiopia with emphasis on the importance of vertical transmission. International Journal of Epidemiology 1988;17(4):874‐9. - PubMed
Xiao 2007 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Xiao XM, Li AZ, Chen X, Zhu YK, Miao J. Prevention of vertical hepatitis B transmission by hepatitis immunoglobulin in the third trimester of pregnancy. Obstetrical and Gynecological Survey 2007;62(8):494‐510.
Xu 1985 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Xu ZY, Liu CB, Francis DP, Purcell RH, Gun ZL, Duan SC, et al. Prevention of perinatal acquisition of hepatitis B virus carriage using vaccine: preliminary report of a randomised, double‐blind placebo‐controlled and comparative trial. Pediatrics 1985;76:713‐8. - PubMed
Xu 2009 {published data only}
-
- Xu WM, Cui YT, Wang L, Yang H, Liang ZQ, Li XM, et al. Lamivudine in late pregnancy to prevent perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus infection: a multicentre, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 2009;16(2):94‐103. - PubMed
Zhang 2005 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Zhang LN, Zou Q, Zhang L. Study on a combined antepartum and postpartum to interrupt the transmission of hepatitis B virus from mother with positive HBsAg to infant. Journal of Chinese Modern Pediatrics 2005;2(6):484‐5.
Zhu 2004 {published data only}
-
- Zhu Q, Yu H, Chen H, Dong Z, Dei L, Gu X, et al. Study on a combined antepartum and postpartum to interrupt the transmission of hepatitis B virus from mother with both positive HBsAg and HBeAg to infant. Chinese Journal of Infectious Disease 2004;22:160‐3.
Additional references
Abou‐Zahr 2003
-
- Abou‐Zahr I, Carla L, Wardlaw T, Tessa M, editors. Ante‐natal Care in Developing Countries: Promises, Achievements and Missed Opportunities: an Analysis of Trends, Levels and Differentials. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO), 2003.
Agbede 2007
-
- Agbede OO, Iseniyi JO, Kolawole MO, Ojuawo A. Risk factors and seroprevalence of hepatitis B surface antigenaemia in mothers and their pre‐school age children in Ilorin, Nigeria. Future Medicine 2007;4(1):67‐72.
Ahn 2010
Almeida 2001
-
- Almeida Neto C, Strauss E, Sabino EC, Sucupira MC, Chamone DA. Significance of isolated hepatitis B core antibody in blood donors from Sao Paulo. Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de Sao Paulo 2001;43(4):203‐8. [PUBMED: 11557999] - PubMed
Angus 2000
-
- Angus PW, McCaughan GW, Gane EJ, Crawford DH, Harley H. Combination low‐dose hepatitis B immune globulin and lamivudine therapy provides effective prophylaxis against posttransplantation hepatitis B. Liver Transplantation 2000;6(4):429‐33. [PUBMED: 10915163] - PubMed
Ayres 2014
-
- Ayres A, Yuen L, Jackson KM, Manoharan S, Glass A, Maley M, et al. Short duration of lamivudine for the prevention of hepatitis B virus transmission in pregnancy: lack of potency and selection of resistance mutations. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 2014;21(11):809‐17. [PUBMED: 24329944] - PubMed
Blumberg 1977
-
- Blumberg BS. Australia antigen and the biology of hepatitis B. Science 1977;197(4298):17‐25. - PubMed
Bodihar 2004
-
- Bodihar NP. Hepatitis B infection in pregnancy. Hepatitis B Annual 2004;1:199‐209.
Bolarinwa 2015
-
- Bolarinwa RA, Aneke JC, Olowookere SA, Salawu L. Seroprevalence of transfusion transmissible viral markers in sickle cell disease patients and healthy controls in Ile‐Ife, South‐Western Nigeria: a case‐control study. Journal of Applied Hematology 2015;6:162‐7.
Borgia 2012
Brown 2016
-
- Brown RS Jr, McMahon BJ, Lok AS, Wong JB, Ahmed AT, Mouchli MA, et al. Antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B viral infection during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2016;63(1):319‐33. [PUBMED: 26565396] - PubMed
Buti 2013
-
- Buti M, Oyaguez I, Lozano V, Casado MA. Cost effectiveness of first‐line oral antiviral therapies for chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review. PharmacoEconomics 2013;31(1):63‐75. [PUBMED: 23329593] - PubMed
CDC 2008
-
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Recommendations for identification and public health management of persons with chronic hepatitis B virus. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Surveillance Summaries : MMWR 2008;57(8):1‐20. - PubMed
Celen 2013
Cui 2011
-
- Cui HY, Zhao CM, Shen XX. The efficacy of hepatitis B combined with HBIG in infants born to HBsAg and HBeAg carrier mothers. Chinese Journal of Disease Control & Prevention 2011;15:545.
del Canho 1994
-
- Canho R, Grosheide PM, Schalm SW, Vries RR, Heijtink RA. Failure of neonatal hepatitis B vaccination: the role of HBV‐DNA levels in hepatitis B carrier mothers and HLA antigens in neonates. Journal of Hepatology 1994;20(4):483‐6. [PUBMED: 8051386] - PubMed
DeMets 1987
-
- DeMets DL. Methods of combining randomized clinical trials: strengths and limitations. Statistics in Medicine 1987;6(3):341‐50. - PubMed
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7(3):177‐88. - PubMed
Eke 2011
Ellis 1969
-
- Ellis EF, Henney CS. Adverse reactions following administration of human gamma globulin. Journal of Allergy 1969;43(1):45‐54. - PubMed
Gambarin‐Gelwel 2007
-
- Gambarin‐Gelwel M. Hepatitis B in pregnancy. Clinics of Liver Disease 2007;11:945‐63. - PubMed
Gentile 2014a
-
- Gentile I, Zappulo E, Buonomo AR, Borgia G. Prevention of mother‐to‐child transmission of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus. Expert Review of Anti‐infective Therapy 2014;12(7):775‐82. [PUBMED: 24840817] - PubMed
Gentile 2014b
Gluud 2016
-
- Gluud C, Nikolova D, Klingenberg SL. Cochrane Hepato‐Biliary Group. About Cochrane (Cochrane Review Groups (CRGs)) 2016, Issue 6. Art. No.: LIVER.
Guo 2013
Guyatt 2008
Guyatt 2011
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Woodcock J, Brozek J, Helfand M, et al. GRADE guidelines: 8. Rating the quality of evidence‐indirectness. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(12):1303‐10. [PUBMED: 21802903] - PubMed
Habib 2007
-
- Habib S, Shaikh OS. Hepatitis B immunoglobulin. Drugs Today 2007;43(6):379. - PubMed
Hadziyannis 1995
-
- Hadziyannis SJ. Hepatitis B e antigen negative chronic hepatitis B: from clinical recognition to pathogenesis and treatment. Viral Hepatitis Review 1995;1:7‐36.
Hadziyannis 2001
-
- Hadziyannis SJ, Vassilopoulos D. Hepatitis B e antigen‐negative chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.) 2001;34(4 Pt 1):617‐24. [PUBMED: 11584355] - PubMed
Han 2007
-
- Han ZH, Zhong LH, Wang J, Zhao QL, Sun YG, Li LW, et al. The impact of antepartum injection of hepatitis B immunoglobulin on maternal serum HBV DNA and anti‐HBs in the newborns. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 2007;46(5):376‐8. [PUBMED: 17637304] - PubMed
Han 2011
-
- Han GR, Cao MK, Zhao W, Jiang HX, Wang CM, Bai SF, et al. A prospective and open‐label study for the efficacy and safety of telbivudine in pregnancy for the prevention of perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus infection. Journal of Hepatology 2011;55(6):1215‐21. [PUBMED: 21703206] - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.handbook.cochrane.org.
ICH‐GCP 1997
-
- International Conference on Harmonisation Expert Working Group. International Conference on Harmonisation of technical requirements for registration of pharmaceuticals for human use. ICH harmonised tripartite guideline. Guideline for good clinical practice CFR & ICH Guidelines. Vol. 1, Philadelphia (PA): Barnett International/PAREXEL, 1997.
Jakobsen 2014
Jin 2014
Kjaergard 2001
-
- Kjaergard LL, Villumsen J, Gluud C. Reported methodologic quality and discrepancies between large and small randomised trials in meta‐analyses. Annals of Internal Medicine 2001;135(11):982‐9. - PubMed
Kumar 2007
-
- Kumar V, Abbas AK, Fausto N, Mitchell RN. Robbins Basic Pathology. 7th Edition. Philadelphia (PA): WB Saunders, 2007.
Lee 2009
Li 2010
-
- Li P, Liu XR, Cheng W, Wang T, Zhou XE. Clinical study on the effect of long period and high dosage HBV immunoglobulin in treatment of preventing HBV's intrauterine spreading. Practical Journal of Clinical Medicine 2010;7(4):30‐1.
Li 2013
-
- Li WG, Zhang JL, Wang HQ. Hepatitis B infection among babies born by pregnant women with different HBV infection status by passive immunization. Modern Preventive Medicine 2013;4:633‐4.
Liu 2009
-
- Liu LZ, Zheng JS, Li Q, Yu XH, Deng W. The study of the significance infection of hepatitis B virus of placenta and fetus in pregnant woman with hepatitis B surface antigen, anti‐HBe and anti‐HBc positive. Acta Academiae Medicinae Jiangxi 2009;49(2):92‐5.
Liu 2015
-
- Liu CP, Zeng YL, Zhou M, Chen LL, Hu R, Wang L, et al. Factors associated with mother‐to‐child transmission of hepatitis B virus despite immunoprophylaxis. Internal Medicine (Tokyo, Japan) 2015;54(7):711‐6. [PUBMED: 25832930] - PubMed
Lock 2007
-
- Lock A, Osborn M. Antiviral options for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2007;57:1030‐4. - PubMed
Lu 2014
-
- Lu YP, Liang XJ, Xiao XM, Huang SM, Liu ZW, Li J, et al. Telbivudine during the second and third trimester of pregnancy interrupts HBV intrauterine transmission: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Clinical Laboratory 2014;60(4):571‐86. [PUBMED: 24779291] - PubMed
Lundh 2012
Ma 2014
-
- Ma L, Alla NR, Li X, Mynbaev OA, Shi Z. Mother‐to‐child transmission of HBV: review of current clinical management and prevention strategies. Reviews in Medical Virology 2014;24(6):396‐406. - PubMed
Mathew 2008
Moher 1998
-
- Moher D, Pham B, Jones A, Cook DJ, Jadad AR, Moher M, et al. Does quality of reports of randomised trials affect estimates of intervention efficacy reported in meta‐analyses?. Lancet 1998;352(9128):609‐13. - PubMed
Page 2016
Pan 2012
-
- Pan CQ, Mi LJ, Bunchorntavakul C, Karsdon J, Huang WM, Singhvi G, et al. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for prevention of vertical transmission of hepatitis B virus infection by highly viremic pregnant women: a case series. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 2012;57(9):2423‐9. [PUBMED: 22543886] - PMC - PubMed
Papaevangelou 2012
-
- Papaevangelou V. Perinatal HBV viremia in newborns of HBsAg(+) mothers is a transient phenomenon that does not necessarily imply HBV infection transmission. Journal of Clinical Virology 2012; Vol. 54, issue 2:202. [PUBMED: 22480540] - PubMed
Peters 2006
-
- Peters JL, Sutton AJ, Jones DR, Abrams KR, Rushton L. Comparison of two methods to detect publication bias in meta‐analysis. JAMA 2006;295(6):676‐80. [PUBMED: 16467236] - PubMed
Rasha 2007
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Rivkina 2002
-
- Rivkina A, Rybalov S. Chronic hepatitis B: current and future treatment options. Pharmacotherapy 2002;22(6):721‐37. - PubMed
Rothstein 1982
-
- Rothstein SS, Goldman HS, Arcomano A. Passive immunization for hepatitis B. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 1982;40(1):34‐7. - PubMed
Royle 2003
-
- Royle P, Milne R. Literature searching for randomised controlled trials used in Cochrane reviews: rapid versus exhaustive searches. International Journal of Technology Assessment in Health Care 2003;19(4):591‐603. - PubMed
Sangkomkamhang 2014
Savović 2012a
-
- Savović J, Jones HE, Altman DG, Harris RJ, Jüni P, Pildal J, et al. Influence of reported study design characteristics on intervention effect estimates from randomized, controlled trials. Health Technology Assessment 2012;16(35):1‐82. - PubMed
Savović 2012b
-
- Savović J, Jones HE, Altman DG, Harris RJ, Jüni P, Pildal J, et al. Influence of reported study design characteristics on intervention effect estimates from randomized, controlled trials. Annals of Internal Medicine 2012;157(6):429‐38. - PubMed
Schillie 2015
-
- Schillie S, Walker T, Veselsky S, Crowley S, Dusek C, Lazaroff J, et al. Outcomes of infants born to women infected with hepatitis B. Pediatrics 2015;135(5):e1141‐7. [PUBMED: 25896839] - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273(5):408‐12. - PubMed
Seow 1999
-
- Seow HF. Hepatitis B and C in pregnancy. Current Obstetrics & Gynaecology 1999;9:216‐23.
Shahnaz 2005
-
- Shahnaz S, Reza B, Seyed‐Moayed A. Risk factors in chronic hepatitis B infection: a case control study. Hepatitis Monthly 2005;5(4):109‐15.
Shi 2010a
-
- Shi Z, Yang Y, Ma L, Li X, Schreiber A. Lamivudine in late pregnancy to interrupt in utero transmission of hepatitis B virus: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2010;116(1):147‐59. [PUBMED: 20567182] - PubMed
Shi 2010b
-
- Shi Z, Li X, Ma L, Yang Y. Hepatitis B immunoglobulin injection in pregnancy to interrupt hepatitis B virus mother‐to‐child transmission ‐ a meta‐analysis. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2010;14(7):e622‐34. - PubMed
Sun 2007
-
- Sun B, Zheng RS, Yu SJ, Liu XL. The efficacy of hepatitis B combined with HBIG in infants born to HBsAg and HBeAg carrier mothers. Chinese Journal of Public Health 2007;23:86‐7.
Szmuness 1981
-
- Szmuness W, Stevens CE, Olesko WR. Passive‐active immunization against hepatitis B: immunogenicity studies in adult Americans. Lancet 1981;1:575‐7. - PubMed
Thorlund 2011
-
- Thorlund K, Engstrøm J, Wetterslev J, Brok J, Imberger G, Gluud C. User manual for Trial Sequential Analysis (TSA). ctu.dk/tsa/files/tsa_manual.pdf 2011 (accessed 23 April 2013).
TSA 2011 [Computer program]
-
- Copenhagen Trial Unit. TSA ‐ Trial Sequential Analysis. Version 0.9 Beta. Copenhagen: Copenhagen Trial Unit, 2011.
Tsai 2014
Visvanathan 2016
-
- Visvanathan K, Dusheiko G, Giles M, Wong ML, Phung N, Walker S, et al. Managing HBV in pregnancy. Prevention, prophylaxis, treatment and follow‐up: position paper produced by Australian, UK and New Zealand key opinion leaders. Gut 2016;65(2):340‐50. [PUBMED: 26475631] - PubMed
Wetterslev 2008
-
- Wetterslev J, Thorlund K, Brok J, Gluud C. Trial sequential analysis may establish when firm evidence is reached in cumulative meta‐analysis. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2008;61(1):64‐75. - PubMed
Wetterslev 2009
WHO 2006
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Immunization against infectious disease. The Green Book 2006;2:51‐70.
Wiseman 2009
-
- Wiseman E, Fraser MA, Holden S, Glass A, Kidson BL, Heron LG, et al. Perinatal transmission of hepatitis B virus: an Australian experience. Journal of the Australian Medical Association 2009; Vol. 190, issue 9:489‐92. - PubMed
Wong 2014
-
- Wong F, Pai R, Schalkwyk J, Yoshida EM. Hepatitis B in pregnancy: a concise review of neonatal vertical transmission and antiviral prophylaxis. Annals of Hepatology 2014;13(2):187‐95. [PUBMED: 24552860] - PubMed
Wood 2008
Xu 2002
-
- Xu DZ, Yan YP, Choi BC, Xu JQ, Men K, Zhang JX, et al. Risk factors and mechanism of transplacental transmission of hepatitis B virus: a case‐control study. Journal of Medical Virology 2002;67(1):20‐6. [PUBMED: 11920813] - PubMed
Xu 2014
-
- Xu H, Zeng T, Liu J‐Y, Lei Y, Zhong S, Sheng Y‐J, et al. Measures to reduce mother‐to‐child transmission of Hepatitis B virus in China: a meta‐analysis. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 2014;59(2):242‐58. - PubMed
Yan 1999
-
- Yan Y, Xu D, Wang W. The role of placenta in hepatitis B virus intrauterine transmission. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 1999;34(7):392‐5. [PUBMED: 11360645] - PubMed
Yan 2009
-
- Yan KH, Li LL, Chen SY, Wu M, Zhu MY, He LL. Assessment of effect of HBIG combined with hepatitis B vaccine in interrupting vertical transmission of HBV from mothers to babies. China Tropical Medicine 2009;9:505‐6.
Yi 2016
-
- Yi P, Chen R, Huang Y, Zhou RR, Fan XG. Management of mother‐to‐child transmission of hepatitis B virus: propositions and challenges. Journal of Clinical Virology 2016;77:32‐9. [PUBMED: 26895227] - PubMed
Yin 2013
-
- Yin Y, Wu L, Zhang J, Zhou J, Zhang P, Hou H. Identification of risk factors associated with immunoprophylaxis failure to prevent the vertical transmission of hepatitis B virus. Journal of Infection 2013;66(5):447‐52. [PUBMED: 23286968] - PubMed
Yuan 2009
-
- Yuan GP, Li MZ, Yu K, Chu GF. Effect of recombinant hepatitis B vaccine combined with hepatitis B immunoglobulin in interruption of vertical transmission of HBV. Chinese Journal of Public Health 2009;12:1479‐80.
Zhang 2004
Zhao 2008
-
- Zhao SK, Lv HY. Effect of hepatitis B vaccine combined with hepatitis B immunoglobulin in interruption of vertical transmission of HBV. Journal of Practical Diagnosis and Therapy 2008;22:236‐7.
Zhou 2012
-
- Zhou Y, Jin H, Liu P. Effect of hepatitis B immunoglobulin intrauterine injection on interrupting hepatitis B virus mother‐to‐child transmission: a systematic review. Chinese Journal of Evidence‐Based Medicine 2012;12(7):791‐8.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

