An improved FSL-FIRST pipeline for subcortical gray matter segmentation to study abnormal brain anatomy using quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM)
- PMID: 28188873
- PMCID: PMC5421359
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mri.2017.02.002
An improved FSL-FIRST pipeline for subcortical gray matter segmentation to study abnormal brain anatomy using quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM)
Abstract
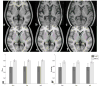
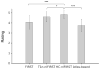
Accurate and robust segmentation of subcortical gray matter (SGM) nuclei is required in many neuroimaging applications. FMRIB's Integrated Registration and Segmentation Tool (FIRST) is one of the most popular software tools for automated subcortical segmentation based on T1-weighted (T1w) images. In this work, we demonstrate that FIRST tends to produce inaccurate SGM segmentation results in the case of abnormal brain anatomy, such as present in atrophied brains, due to a poor spatial match of the subcortical structures with the training data in the MNI space as well as due to insufficient contrast of SGM structures on T1w images. Consequently, such deviations from the average brain anatomy may introduce analysis bias in clinical studies, which may not always be obvious and potentially remain unidentified. To improve the segmentation of subcortical nuclei, we propose to use FIRST in combination with a special Hybrid image Contrast (HC) and Non-Linear (nl) registration module (HC-nlFIRST), where the hybrid image contrast is derived from T1w images and magnetic susceptibility maps to create subcortical contrast that is similar to that in the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) template. In our approach, a nonlinear registration replaces FIRST's default linear registration, yielding a more accurate alignment of the input data to the MNI template. We evaluated our method on 82 subjects with particularly abnormal brain anatomy, selected from a database of >2000 clinical cases. Qualitative and quantitative analyses revealed that HC-nlFIRST provides improved segmentation compared to the default FIRST method.
Keywords: Brain; FIRST; MRI; Quantitative susceptibility mapping; Segmentation; Subcortical gray matter.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures








References
-
- Fischl B, Salat DH, Busa E, Albert M, Dieterich M, Haselgrove C, et al. Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron. 2002;33(3):341–55. - PubMed
-
- Fischl B, Salat DH, van der Kouwe AJ, Makris N, Segonne F, Quinn BT, et al. Sequence-independent segmentation of magnetic resonance images. NeuroImage. 2004;23(Suppl 1):69–84. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

