Synthesis and opioid receptor binding of indium (III) and [111In]-labeled macrocyclic conjugates of diprenorphine: novel ligands designed for imaging studies of peripheral opioid receptors
- PMID: 28190898
- PMCID: PMC5298243
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tet.2016.08.015
Synthesis and opioid receptor binding of indium (III) and [111In]-labeled macrocyclic conjugates of diprenorphine: novel ligands designed for imaging studies of peripheral opioid receptors
Abstract
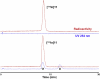
Radiolabeled diprenorphine (DPN) and analogs are widely used ligands for non-invasive brain imaging of opioid receptors. To develop complementary radioligands optimized for studies of the peripheral opioid receptors, we prepared a pair of hydrophilic DPN derivatives, conjugated to the macrocyclic chelator DOTA (1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid), for complexation with trivalent metals. The non-radioactive indium (III) complexes, tethered to the C6-oxygen position of the DPN scaffold by 6- to 9-atom spacers, displayed high affinities for binding to μ, δ and κ opioid receptors in vitro. Use of the 9-atom linker conferred picomolar affinities equipotent to those of the parent ligand DPN. The [111In]-labeled complexes were prepared in good yield (>70%), with high radiochemical purity (~99%) and high specific radioactivity (>4000 mCi/μmol). Their log D7.4 values were -2.21 to -1.66. In comparison, DPN is lipophilic, with a log D7.4 of +2.25. Further study in vivo is warranted to assess the suitability of these [111In]-labeled DPN-DOTA conjugates for imaging trials.
Keywords: Bioconjugate; Diprenorphine; Imaging; Opioid receptor; Radiometal.
Figures



References
-
- Lever JR. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007;13:33–49. - PubMed
-
- Dannals RF. J. Label. Comp. Radiopharm. 2013;56:187–195. - PubMed
-
- van Waarde A, Absalom AR, Visser AK, Dierckx RA. In: PET and SPECT of Neurobiological Systems. Dierckx, Rudi AJO, Otte A, de Vries EFJ, van Waarde A, Luiten PGM, editors. Springer; Berlin, Heidelberg: 2014. pp. 585–623.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
