Defective IL-23/IL-17 Axis Protects p47phox-/- Mice from Colon Cancer
- PMID: 28191009
- PMCID: PMC5271172
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00044
Defective IL-23/IL-17 Axis Protects p47phox-/- Mice from Colon Cancer
Abstract
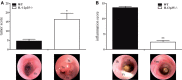
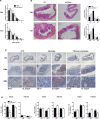
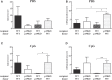
In the colon, a sophisticated balance between immune reaction and tolerance is absolutely required. Dysfunction may lead to pathologic phenotypes ranging from chronic inflammatory processes to cancer development. Two prominent modulators of colon inflammation are represented by the closely related cytokines interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-23, which initiate adaptive Th1 and Th17 immune responses, respectively. In this study, we investigated the impact of the NADPH oxidase protein p47phox, which negatively regulates IL-12 in dendritic cells, on colon cancer development in a colitis-associated colon cancer model. Initially, we found that IL-12-/- mice developed less severe colitis but are highly susceptible to colon cancer. By contrast, p47phox-/- mice showed lower tumor scores and fewer high grade tumors than wild-type (WT) littermates. Treatment with toll-like receptor 9 ligand CpG2216 significantly enhanced colitis in p47phox-/- mice, whereas tumor growth was simultaneously reduced. In tumor tissue of p47phox-/- mice, the IL-23/IL-17 axis was crucially hampered. IL-23p19 protein expression in tumor tissue correlated with tumor stage. Reconstitution of WT mice with IL-23p19-/- bone marrow protected these mice from colon cancer, whereas transplantation of WT hematopoiesis into IL-23p19-/- mice increased the susceptibility to tumor growth. Our study strengthens the divergent role of IL-12 and IL-23 in colon cancer development. With the characterization of p47phox as a novel modulator of both cytokines our investigation introduces a promising new target for antitumor strategies.
Keywords: DSS/AOM; IL-17; IL-23; IL23p19 knockout mouse; chronic colitis; colon cancer; p47phox.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

