Blaming the Brain for Obesity: Integration of Hedonic and Homeostatic Mechanisms
- PMID: 28192106
- PMCID: PMC5406238
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.12.050
Blaming the Brain for Obesity: Integration of Hedonic and Homeostatic Mechanisms
Abstract
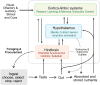
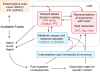
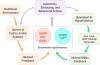
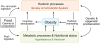
The brain plays a key role in the controls of energy intake and expenditure, and many genes associated with obesity are expressed in the central nervous system. Technological and conceptual advances in both basic and clinical neurosciences have expanded the traditional view of homeostatic regulation of body weight by mainly the hypothalamus to include hedonic controls of appetite by cortical and subcortical brain areas processing external sensory information, reward, cognition, and executive functions. Hedonic controls interact with homeostatic controls to regulate body weight in a flexible and adaptive manner that takes environmental conditions into account. This new conceptual framework has several important implications for the treatment of obesity. Because much of this interactive neural processing is outside awareness, cognitive restraint in a world of plenty is made difficult and prevention and treatment of obesity should be more rationally directed to the complex and often redundant mechanisms underlying this interaction.
Keywords: Appetite; Cognition; Cortex; Hypothalamus; Limbic System; Physical Activity; Reward; Self-Control.
Copyright © 2017 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Hess W. Das Zwischenhirn: Syndrome, Localisationen, Funktionen. Basel: Schwabe; 1949.
-
- Brobeck JR. Mechanism of the development of obesity in animals with hypothalamic lesions. Physiol Rev. 1946;26:541–59. - PubMed
-
- Bruegger M. Fresstrieb als hypothalamisches Syndrom. Helvetica Physiologica Acta. 1943;1:183–198.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

