Review of metabolic pathways activated in cancer cells as determined through isotopic labeling and network analysis
- PMID: 28192215
- PMCID: PMC5552450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymben.2017.02.002
Review of metabolic pathways activated in cancer cells as determined through isotopic labeling and network analysis
Abstract
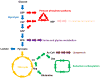
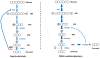
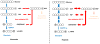
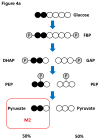
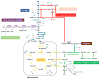
Cancer metabolism has emerged as an indispensable part of contemporary cancer research. During the past 10 years, the use of stable isotopic tracers and network analysis have unveiled a number of metabolic pathways activated in cancer cells. Here, we review such pathways along with the particular tracers and labeling observations that led to the discovery of their rewiring in cancer cells. The list of such pathways comprises the reductive metabolism of glutamine, altered glycolysis, serine and glycine metabolism, mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) induced reprogramming and the onset of acetate metabolism. Additionally, we demonstrate the critical role of isotopic labeling and network analysis in identifying these pathways. The alterations described in this review do not constitute a complete list, and future research using these powerful tools is likely to discover other cancer-related pathways and new metabolic targets for cancer therapy.
Keywords: Cancer metabolism; Isotopic labeling analysis.
Copyright © 2017 International Metabolic Engineering Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Ahn WS, Zhang Z, Cantor JR, Iliopoulos O, Stephanopoulos G. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase modulates non-oxidative pentose phosphate pathway to provide anabolic precursors in hypoxic tumor cells. n.d Under Review.
-
- Amelio I, Cutruzzolá F, Antonov A, Agostini M, Melino G. Serine and glycine metabolism in cancer. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 2014;39(4):191–198. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2014.02.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barbosa MJ, Rocha JMS, Tramper J, Wijffels RH. Acetate as a carbon source for hydrogen production by photosynthetic bacteria. Journal of Biotechnology. 2001;85(1):25–33. http://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1656(00)00368-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Basan M, Hui S, Okano H, Zhang Z, Shen Y, Williamson JR, Hwa T. Overflow metabolism in Escherichia coli results from efficient proteome allocation. Nature. 2015;528(7580):99–104. http://doi.org/10.1038/nature15765. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Birsoy K, Wang T, Chen WW, Freinkman E, Abu-Remaileh M, Sabatini DM. An Essential Role of the Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain in Cell Proliferation Is to Enable Aspartate Synthesis. Cell. 2015;162(3):540–551. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.07.016. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

