m6A-dependent maternal mRNA clearance facilitates zebrafish maternal-to-zygotic transition
- PMID: 28192787
- PMCID: PMC5323276
- DOI: 10.1038/nature21355
m6A-dependent maternal mRNA clearance facilitates zebrafish maternal-to-zygotic transition
Abstract
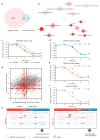
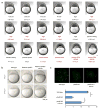
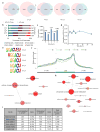
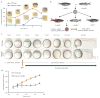
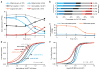
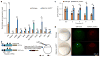
The maternal-to-zygotic transition (MZT) is one of the most profound and tightly orchestrated processes during the early life of embryos, yet factors that shape the temporal pattern of vertebrate MZT are largely unknown. Here we show that over one-third of zebrafish maternal messenger RNAs (mRNAs) can be N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modified, and the clearance of these maternal mRNAs is facilitated by an m6A-binding protein, Ythdf2. Removal of Ythdf2 in zebrafish embryos decelerates the decay of m6A-modified maternal mRNAs and impedes zygotic genome activation. These embryos fail to initiate timely MZT, undergo cell-cycle pause, and remain developmentally delayed throughout larval life. Our study reveals m6A-dependent RNA decay as a previously unidentified maternally driven mechanism that regulates maternal mRNA clearance during zebrafish MZT, highlighting the critical role of m6A mRNA methylation in transcriptome switching and animal development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

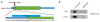

Comment in
-
RNA Methylation Clears the Way.Dev Cell. 2017 Mar 13;40(5):427-428. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.02.024. Dev Cell. 2017. PMID: 28292421
-
Mark it for destruction: a novel role of mRNA methylation in maternal-to-zygotic transition†.Biol Reprod. 2017 Apr 1;96(4):829-830. doi: 10.1093/biolre/iox016. Biol Reprod. 2017. PMID: 28371885 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Tadros W, Lipshitz HD. The maternal-to-zygotic transition: a play in two acts. Development. 2009;136:3033–3042. - PubMed
-
- Walser CB, Lipshitz HD. Transcript clearance during the maternal-to-zygotic transition. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2011;21:431–443. - PubMed
-
- Giraldez AJ, et al. Zebrafish miR-430 promotes deadenylation and clearance of maternal mRNAs. Science. 2006;312:75–79. - PubMed
-
- Mishima Y, Tomari Y. Codon usage and 3′UTR length determine maternal mRNA stability in zebrafish. Mol Cell. 2016;61:874–885. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

