Evaluation of quality of life in adults with neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) using the Impact of NF1 on Quality Of Life (INF1-QOL) questionnaire
- PMID: 28193237
- PMCID: PMC5307827
- DOI: 10.1186/s12955-017-0607-y
Evaluation of quality of life in adults with neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) using the Impact of NF1 on Quality Of Life (INF1-QOL) questionnaire
Abstract
Background: Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) is an inherited, multi-system, tumour suppressor disorder with variable complications that cause psychological distress and social isolation. The study aim was to develop and validate a disease-specific questionnaire to measure quality of life (QOL) in NF1 that is suitable both as an assessment tool in clinical practice and in clinical trials of novel therapy.
Methods: The Impact of NF1 on Quality of Life (INF1-QOL) questionnaire was developed by a literature search for common terms, focus group (n = 6), semi-structured interviews (n = 21), initial drafts (n =50) and final 14 item questionnaire (n = 50). Bivariate correlations between items, exploratory factor analysis, correlations with severity and EuroQol were employed.
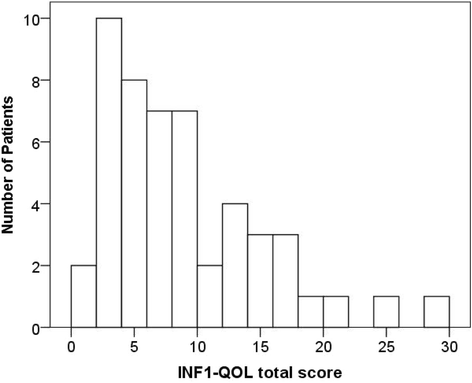
Results: INF1-QOL showed good internal reliability (Cronbach's alpha 0.87), mean total INF1-QOL score was 8.64 (SD 6.3), median 7.00, range 0-30 (possible range 0-42); no significant correlations with age or gender. The mean total EuroQol score was 7.38 (SD 2.87), median 6.5, mean global EuroQol score was 76.34 (SD 16.56), median 80. Total INF1-QOL score correlated with total EuroQol r = 0.82, p < 0.0001. The highest impact on QOL was moderate or severe problems with anxiety and depression (32%) and negative effects of NF1 on role and outlook on life (42%). The mean inter-relater reliability for grading of clinical severity scores was 0.71 (range 0.65-0.79), and intra-class correlation was 0.92. The mean clinical severity score was 1.95 (SD 0.65) correlating r = 0.34 with total INF1-QOL score p < 0.05 and correlated 0.37 with total EuroQol score p < 0.01. The clinical severity score was mild in 17 (34%), moderate in 16 (32%) and 17 (34%) individuals had severe disease.
Conclusions: INF1-QOL is a validated, reliable disease specific questionnaire that is easy and quick to complete. Role and outlook on life and anxiety and depression have the highest impact on QOL indicating the variability, severity and unpredictability of NF1. INFI-QOL correlates moderately with clinical severity. The moderate relationship between INF1-QOL and physician rated severity emphasizes the difference between clinical and patient perception. INFI-QOL will be useful in individual patient assessment and as an outcome measure for clinical trials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Food-related Quality of Life in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Development and Validation of a Questionnaire.J Crohns Colitis. 2016 Feb;10(2):194-201. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjv192. Epub 2015 Oct 27. J Crohns Colitis. 2016. PMID: 26507859
-
Association of sociodemographic and clinical factors with the quality of life of Brazilian individuals with Neurofibromatosis type 1: a cross-sectional study.An Bras Dermatol. 2024 Jul-Aug;99(4):520-526. doi: 10.1016/j.abd.2023.08.011. Epub 2024 Mar 16. An Bras Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38493052 Free PMC article.
-
Development of the adult PedsQL™ neurofibromatosis type 1 module: initial feasibility, reliability and validity.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2013 Feb 21;11:21. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-11-21. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2013. PMID: 23432799 Free PMC article.
-
The development and validation of the Cluster Headache Quality of life scale (CHQ).J Headache Pain. 2016 Dec;17(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s10194-016-0674-1. Epub 2016 Sep 5. J Headache Pain. 2016. PMID: 27596922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychosocial Features of Neurofibromatosis Type 1 in Children and Adolescents.J Child Neurol. 2018 Mar;33(3):225-232. doi: 10.1177/0883073817749367. Epub 2018 Jan 10. J Child Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29318935 Review.
Cited by
-
Safety and efficacy of selumetinib in pediatric and adult patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 and plexiform neurofibroma.Neuro Oncol. 2024 Dec 5;26(12):2352-2363. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noae121. Neuro Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38975694 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Neurofibromatosis 1 French national guidelines based on an extensive literature review since 1966.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020 Feb 3;15(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s13023-020-1310-3. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020. PMID: 32014052 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of CRMP2 Post-Translational Modifications Drive Its Pathological Functions.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Oct;56(10):6736-6755. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-1568-4. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30915713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas9 editing of Nf1 gene identifies CRMP2 as a therapeutic target in neurofibromatosis type 1-related pain that is reversed by (S)-Lacosamide.Pain. 2017 Dec;158(12):2301-2319. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001002. Pain. 2017. PMID: 28809766 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of neurofibromatosis type 1 on quality of life using the Skindex-29 questionnaire quality of life in NF1.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024 Feb 24;19(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13023-024-03078-0. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024. PMID: 38402381 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferner RE. Psychological impact of the Neurofibromatoses. In: Ferner RE, Huson SM, Evans DG. London: Neurofibromatoses in clinical practice Springer; 2011. p129-140.
-
- Jessen WJ, Miller SJ, Jousma E, Wu J, Rizvi TA, Brundage ME, Eaves D, Widemann B, Kim MO, Dombi E, Sabo J, Hardiman Dudley A, Niwa-Kawakita M, Page GP, Giovannini M, Aronow BJ, Cripe TP, Ratner N. MEK inhibition exhibits efficacy in human and mouse neurofibromatosis tumors. J Clin Invest. 2013;23:340–7. doi: 10.1172/JCI60578. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dombi E, Baldwin A, Marcus LJ, Fisher MJ, Weiss B, Kim A, Whitcomb P, Martin S, Aschbacher-Smith LE, Rizvi TA, Wu J, Ershler R, Wolters P, Therrien J, Glod J, Belasco JB, Schorry E, Brofferio A, Starosta AJ, Gillespie A, Doyle AL, Ratner N, Widemann BC. Activity of Selumetinib in Neurofibromatosis Type 1-Related Plexiform Neurofibromas. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:2550–60. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1605943. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous