Buformin inhibits the stemness of erbB-2-overexpressing breast cancer cells and premalignant mammary tissues of MMTV-erbB-2 transgenic mice
- PMID: 28193239
- PMCID: PMC5307817
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-017-0498-0
Buformin inhibits the stemness of erbB-2-overexpressing breast cancer cells and premalignant mammary tissues of MMTV-erbB-2 transgenic mice
Abstract
Background: Metformin, an FDA-approved drug for the treatment of Type II diabetes, has emerged as a promising anti-cancer agent. Other biguanide analogs, including buformin and phenformin, are suggested to have similar properties. Although buformin was shown to reduce mammary tumor burden in carcinogen models, the anti-cancer effects of buformin on different breast cancer subtypes and the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the effects of buformin on erbB-2-overexpressing breast cancer with in vitro and in vivo models.
Methods: MTT, cell cycle, clonogenic/CFC, ALDEFLUOR, tumorsphere, and Western blot analyses were used to determine the effects of buformin on cell growth, stem cell populations, stem cell-like properties, and signaling pathways in SKBR3 and BT474 erbB-2-overexpressing breast cancer cell lines. A syngeneic tumor cell transplantation model inoculating MMTV-erbB-2 mice with 78617 mouse mammary tumor cells was used to study the effects of buformin (1.2 g buformin/kg chow) on tumor growth in vivo. MMTV-erbB-2 mice were also fed buformin for 10 weeks, followed by analysis of premalignant mammary tissues for changes in morphological development, mammary epithelial cell (MEC) populations, and signaling pathways.
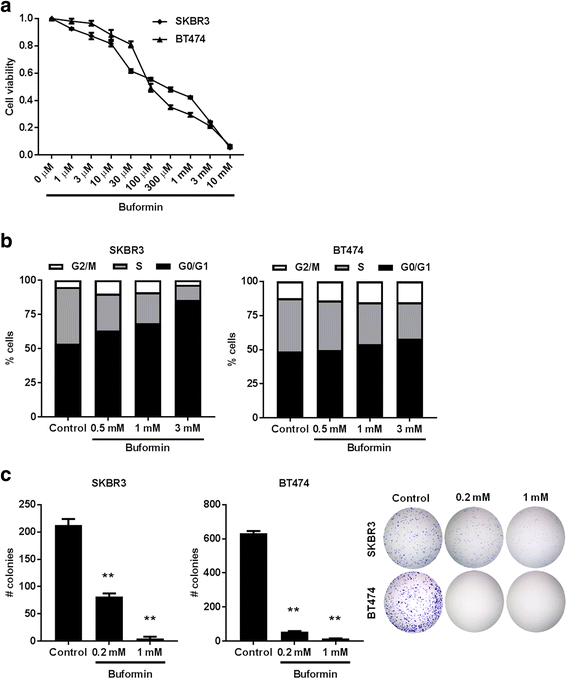
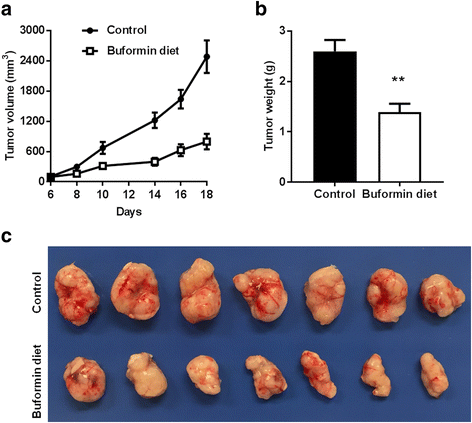
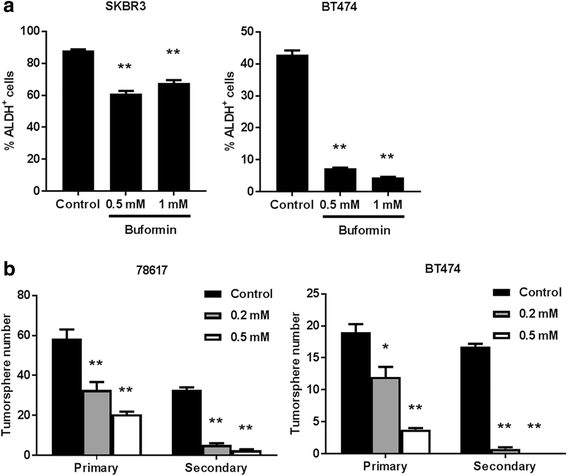
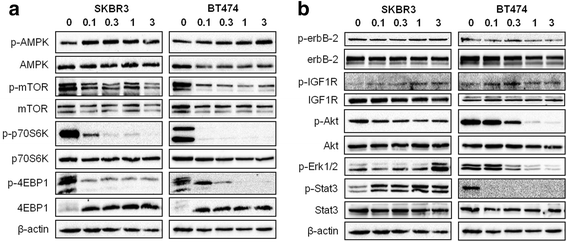
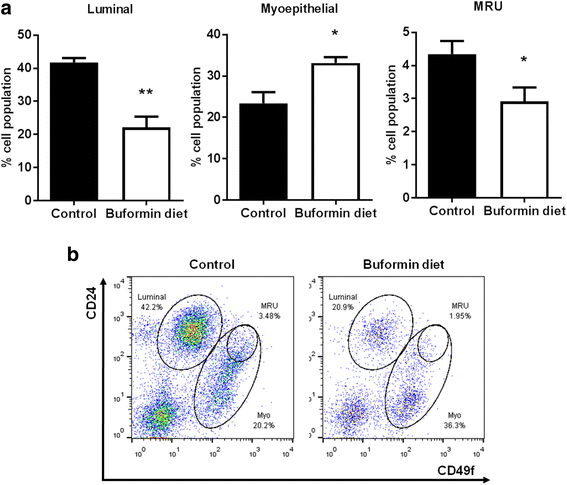
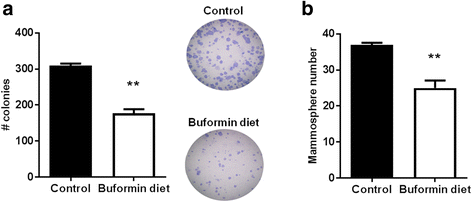
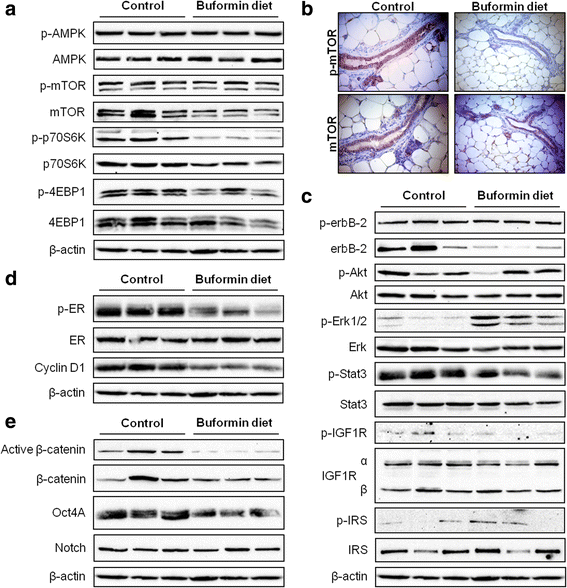
Results: Buformin significantly inhibited SKBR3 and BT474 cell growth, and in vivo activity was demonstrated by considerable growth inhibition of syngeneic tumors derived from MMTV-erbB-2 mice. In particular, buformin suppressed stem cell populations and self-renewal in vitro, which was associated with inhibited receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) and mTOR signaling. Consistent with in vitro data, buformin suppressed mammary morphogenesis and reduced cell proliferation in MMTV-erbB-2 mice. Importantly, buformin decreased MEC populations enriched with mammary reconstitution units (MRUs) and tumor-initiating cells (TICs) from MMTV-erbB-2 mice, as supported by impaired clonogenic and mammosphere formation in primary MECs. We further demonstrated that buformin-mediated in vivo inhibition of MEC stemness is associated with suppressed activation of mTOR, RTK, ER, and β-catenin signaling pathways.
Conclusions: Overall, our results provide evidence for buformin as an effective anti-cancer drug that selectively targets TICs, and present a novel prevention and/or treatment strategy for patients who are genetically predisposed to erbB-2-overexpressing breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Buformin; Cancer stem cells; ErbB-2; Mammary epithelial cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Short-term early exposure to lapatinib confers lifelong protection from mammary tumor development in MMTV-erbB-2 transgenic mice.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Jan 6;36(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0479-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28061785 Free PMC article.
-
FGFR inhibitor, AZD4547, impedes the stemness of mammary epithelial cells in the premalignant tissues of MMTV-ErbB2 transgenic mice.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 12;7(1):11306. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11751-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28900173 Free PMC article.
-
Caloric restriction inhibits mammary tumorigenesis in MMTV-ErbB2 transgenic mice through the suppression of ER and ErbB2 pathways and inhibition of epithelial cell stemness in premalignant mammary tissues.Carcinogenesis. 2018 Oct 8;39(10):1264-1273. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgy096. Carcinogenesis. 2018. PMID: 30107476 Free PMC article.
-
Hormonally up-regulated neu-associated kinase: A novel target for breast cancer progression.Pharmacol Res. 2017 May;119:188-194. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.02.007. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 28189783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implications of the cancer stem-cell hypothesis for breast cancer prevention and therapy.J Clin Oncol. 2008 Jun 10;26(17):2813-20. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.16.3931. J Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18539959 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metformin reduces basal subpopulation and attenuates mammary epithelial cell stemness in FVB/N mice.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jul 11;12:1427395. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1427395. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39055652 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the mTOR pathway in breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs): mechanisms and therapeutic potentials.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Mar 29;16(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04218-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40158191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of ErbB2 breast cancer by mitochondrial targeting.Cancer Metab. 2020 Jul 14;8:17. doi: 10.1186/s40170-020-00223-8. eCollection 2020. Cancer Metab. 2020. PMID: 32695336 Free PMC article.
-
Buformin suppresses osteosarcoma via targeting AMPK signaling pathway.Open Life Sci. 2020 Jun 30;15(1):409-417. doi: 10.1515/biol-2020-0041. eCollection 2020. Open Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 33817229 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing non-oncology small-molecule drugs to improve cancer therapy: Current situation and future directions.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Feb;12(2):532-557. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.09.006. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35256933 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fisher B, Costantino JP, Wickerham DL, Redmond CK, Kavanah M, Cronin WM, Vogel V, Robidoux A, Dimitrov N, Atkins J. Tamoxifen for prevention of breast cancer: report of the national surgical adjuvant breast and bowel project P-1 study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998;90:1371–1388. doi: 10.1093/jnci/90.18.1371. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

