Possible mechanisms for sensorineural hearing loss and deafness in patients with propionic acidemia
- PMID: 28193246
- PMCID: PMC5307832
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-017-0585-5
Possible mechanisms for sensorineural hearing loss and deafness in patients with propionic acidemia
Abstract
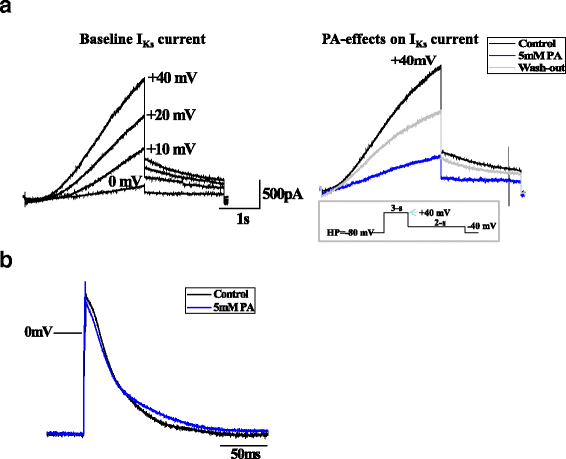
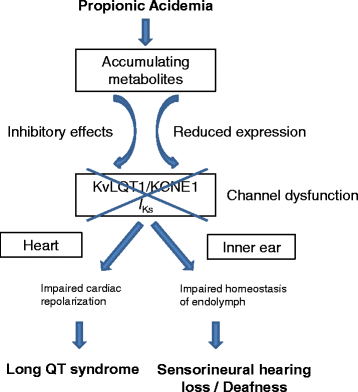
Propionic acidemia is an inborn error of metabolism caused by deficiency of the mitochondrial enzyme propionyl-CoA carboxylase. Sensorineural deafness and severe hearing loss have been described as long-term complications of this disease, however, the mechanism has not yet been elucidated. We have recently shown by patch clamping experiments and Western blots that acute and chronic effects of accumulating metabolites such as propionic acid, propionylcarnitine and methylcitrate on the KvLQT1/KCNE1 channel complex cause long QT syndrome in patients with propionic acidemia by inhibition of K+ flow via this channel. The same KvLQT1/KCNE1 channel complex is expressed in the inner ear and essential for luminal potassium secretion into the endolymphatic space. A disruption of this K+ flow results in sensorineural hearing loss or deafness. It can be assumed that acute and chronic effects of accumulating metabolites on the KvLQT1/KCNE1 channel protein may similarly cause the hearing impairment of patients with propionic acidemia.
Keywords: Hearing loss; Inner ear; KCNE1; KvLQT1; Long QT syndrome; Propionic acidemia; Propionic aciduria; Sensorineural deafness; Voltage-gated potassium channel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of acquired long QT syndrome in patients with propionic academia.Heart Rhythm. 2016 Jun;13(6):1335-45. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2016.02.003. Epub 2016 Feb 27. Heart Rhythm. 2016. PMID: 26854997
-
Deafness in LIMP2-deficient mice due to early loss of the potassium channel KCNQ1/KCNE1 in marginal cells of the stria vascularis.J Physiol. 2006 Oct 1;576(Pt 1):73-86. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.116889. Epub 2006 Aug 10. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16901941 Free PMC article.
-
[Propionic acidemia and sensorineural hearing loss: is there a connection at the molecular genetics level?].HNO. 2008 Jan;56(1):37-42. doi: 10.1007/s00106-007-1560-6. HNO. 2008. PMID: 17415538 German.
-
KCNE1 and KCNE3: The yin and yang of voltage-gated K(+) channel regulation.Gene. 2016 Jan 15;576(1 Pt 1):1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.09.059. Epub 2015 Sep 26. Gene. 2016. PMID: 26410412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of abnormal trafficking of KCNE1 in long QT syndrome 5.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Nov;35(Pt 5):1074-6. doi: 10.1042/BST0351074. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 17956282 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical and biochemical footprints of inherited metabolic diseases. IX. Metabolic ear disease.Mol Genet Metab. 2022 Nov;137(3):223-229. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2022.09.005. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Mol Genet Metab. 2022. PMID: 36183456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathophysiological mechanisms of complications associated with propionic acidemia.Pharmacol Ther. 2023 Sep;249:108501. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108501. Epub 2023 Jul 22. Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37482098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutational and phenotypic spectra of KCNE1 deficiency in Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome and Romano-Ward Syndrome.Hum Mutat. 2019 Feb;40(2):162-176. doi: 10.1002/humu.23689. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Hum Mutat. 2019. PMID: 30461122 Free PMC article.
-
Organic acidurias in adults: late complications and management.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2018 Sep;41(5):765-776. doi: 10.1007/s10545-017-0135-2. Epub 2018 Jan 15. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2018. PMID: 29335813 Review.
-
Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of methylmalonic acidaemia and propionic acidaemia: First revision.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2021 May;44(3):566-592. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12370. Epub 2021 Mar 9. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2021. PMID: 33595124 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fenton W, Gravel W, Rosenblatt D. Disorders of propionate and methylmalonate metabolism. In: Scriver C, Beaudet A, Sly W, Valle D, editors. The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited diseases. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2001. pp. 2165–93.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

