Bile acids potentiate proton-activated currents in Xenopus laevis oocytes expressing human acid-sensing ion channel (ASIC1a)
- PMID: 28193786
- PMCID: PMC5309578
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.13132
Bile acids potentiate proton-activated currents in Xenopus laevis oocytes expressing human acid-sensing ion channel (ASIC1a)
Abstract
Acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) are nonvoltage-gated sodium channels transiently activated by extracellular protons and belong to the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC)/Degenerin (DEG) family of ion channels. Bile acids have been shown to activate two members of this family, the bile acid-sensitive ion channel (BASIC) and ENaC. To investigate whether bile acids also modulate ASIC function, human ASIC1a was heterologously expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Exposing oocytes to tauro-conjugated cholic (t-CA), deoxycholic (t-DCA), and chenodeoxycholic (t-CDCA) acid at pH 7.4 did not activate ASIC1a-mediated whole-cell currents. However, in ASIC1a expressing oocytes the whole-cell currents elicited by pH 5.5 were significantly increased in the presence of these bile acids. Single-channel recordings in outside-out patches confirmed that t-DCA enhanced the stimulatory effect of pH 5.5 on ASIC1a channel activity. Interestingly, t-DCA reduced single-channel current amplitude by ~15% which suggests an interaction of t-DCA with a region close to the channel pore. Molecular docking predicted binding of bile acids to the pore region near the degenerin site (G433) in the open conformation of the channel. Site-directed mutagenesis demonstrated that the amino acid residue G433 is critically involved in the potentiating effect of bile acids on ASIC1a activation by protons.
Keywords: Acid‐sensing ion channel 1a (ASIC1a); bile acids; degenerin site; patch clamp.
© 2017 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Figures
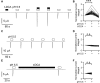
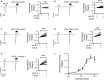
 ) and
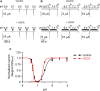
) and  ). For activation curves the current integral values (Q) elicited by pulses of
). For activation curves the current integral values (Q) elicited by pulses of 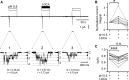
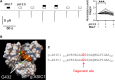
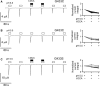
References
-
- Canessa, C. M. 2007. Structural biology: unexpected opening. Nature 449:293–294. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

