Essential role of immobilized chemokine CXCL12 in the regulation of the humoral immune response
- PMID: 28193885
- PMCID: PMC5338526
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1611958114
Essential role of immobilized chemokine CXCL12 in the regulation of the humoral immune response
Abstract
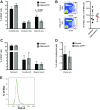
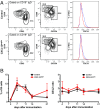
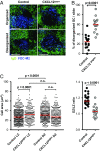
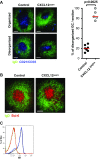
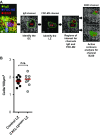
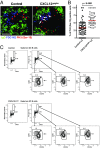
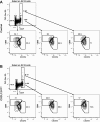
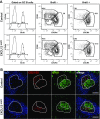
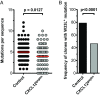
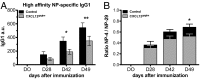
Chemokines control the migration of a large array of cells by binding to specific receptors on cell surfaces. The biological function of chemokines also depends on interactions between nonreceptor binding domains and proteoglycans, which mediate chemokine immobilization on cellular or extracellular surfaces and formation of fixed gradients. Chemokine gradients regulate synchronous cell motility and integrin-dependent cell adhesion. Of the various chemokines, CXCL12 has a unique structure because its receptor-binding domain is distinct and does not overlap with the immobilization domains. Although CXCL12 is known to be essential for the germinal center (GC) response, the role of its immobilization in biological functions has never been addressed. In this work, we investigated the unexplored paradigm of CXCL12 immobilization during the germinal center reaction, a fundamental process where cellular traffic is crucial for the quality of humoral immune responses. We show that the structure of murine germinal centers and the localization of GC B cells are impaired when CXCL12 is unable to bind to cellular or extracellular surfaces. In such mice, B cells carry fewer somatic mutations in Ig genes and are impaired in affinity maturation. Therefore, immobilization of CXCL12 is necessary for proper trafficking of B cells during GC reaction and for optimal humoral immune responses.
Keywords: CXCL12; germinal center reaction; humoral immune responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cyster JG. Chemokines and cell migration in secondary lymphoid organs. Science. 1999;286(5447):2098–2102. - PubMed
-
- Campbell JJ, et al. Chemokines and the arrest of lymphocytes rolling under flow conditions. Science. 1998;279(5349):381–384. - PubMed
-
- Laguri C, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Lortat-Jacob H. Relationships between glycosaminoglycan and receptor binding sites in chemokines-the CXCL12 example. Carbohydr Res. 2008;343(12):2018–2023. - PubMed
-
- Schumann K, et al. Immobilized chemokine fields and soluble chemokine gradients cooperatively shape migration patterns of dendritic cells. Immunity. 2010;32(5):703–713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

