Is low-molecular-weight heparin beneficial to chronic ulcers? A meta-analysis of randomised control trials
- PMID: 28194882
- PMCID: PMC7950054
- DOI: 10.1111/iwj.12708
Is low-molecular-weight heparin beneficial to chronic ulcers? A meta-analysis of randomised control trials
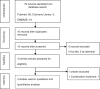
Figures
References
-
- Serra R, Buffone G, de Franciscis A, Mastrangelo D, Vitagliano T, Greco M, de Franciscis S. Skin grafting followed by low‐molecular‐weight heparin long‐term therapy in chronic venous leg ulcers. Ann Vasc Surg 2012;26:190–7. - PubMed
-
- Rullan M, Cerdà L, Frontera G, Masmiquel L, Llobera J. Treatment of chronic diabetic foot ulcers with bemiparin: a randomized, triple‐blind, placebo‐controlled, clinical trial. Diabet Med 2008;25:1090–5. - PubMed
-
- Kalani M, Apelqvist J, Blombäck M, Brismar K, Eliasson B, Eriksson JW, Fagrell B, Hamsten A, Torffvit O, Jörneskog G. Effect of dalteparin on healing of chronic foot ulcers in diabetic patients with peripheral arterial occlusive disease: a prospective, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Diabetes Care 2003;26:2575–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical