GSK-3β Inhibition Induced Neuroprotection, Regeneration, and Functional Recovery After Intracerebral Hemorrhagic Stroke
- PMID: 28195036
- PMCID: PMC5657706
- DOI: 10.3727/096368916X694364
GSK-3β Inhibition Induced Neuroprotection, Regeneration, and Functional Recovery After Intracerebral Hemorrhagic Stroke
Abstract
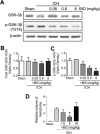
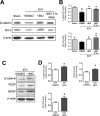
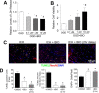
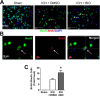
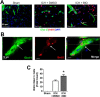
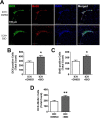
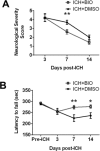
Hemorrhagic stroke is a devastating disease that lacks effective therapies. In the present investigation, we tested 6-bromoindirubin-3'-oxime (BIO) as a selective glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) inhibitor in a mouse model of intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). ICH was induced by injection of collagenase IV into the striatum of 8- to 10-week-old C57BL/6 mice. BIO (8 μg/kg, IP) was administered following either an acute delivery (0-2 h delay) or a prolonged regimen (every 48 h starting at 3 days post-ICH). At 2 days post-ICH, the acute BIO treatment significantly reduced the hematoma volume. In the perihematoma regions, BIO administration blocked GSK-3β phosphorylation/activation, increased Bcl-2 and β-catenin levels, and significantly increased viability of neurons and other cell types. The prolonged BIO regimen maintained a higher level of β-catenin, upregulated VEGF and BDNF, and promoted neurogenesis and angiogenesis in peri-injury zones at 14 days after ICH. The BIO treatment also promoted proliferation of neural stem cells (NSCs) and migration of nascent DCX+ neuroblasts from the subventricular zone (SVZ) to the lesioned cortex. BIO improved functional outcomes on both the neurological severity score and rotarod tests. The findings of this study corroborate the neuroprotective and regenerative effects of BIO and suggest that the Wnt/GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway may be explored for the treatment of acute or chronic ICH.
Figures
References
-
- Rosamond W, Flegal K, Furie K, Go A, Greenlund K, Haase N, Hailpern SM, Ho M, Howard V, Kissela B, Kittner S, Lloyd-Jones D, McDermott M, Meigs J, Moy C, Nichol G, O'Donnell C, Roger V, Sorlie P, Steinberger J, Thom T, Wilson M, Hong Y; and for the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics–-2008 update: A report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation 2008; 117(4): e25–146. - PubMed
-
- Sacco S, Marini C, Toni D, Olivieri L, Carolei A. Incidence and 10-year survival of intracerebral hemorrhage in a population-based registry. Stroke 2009; 40(2): 394–9. - PubMed
-
- van Asch CJ, Luitse MJ, Rinkel GJ, van der Tweel I, Algra A, Klijn CJ,. Incidence, case fatality, and functional outcome of intracerebral haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and ethnic origin: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2010; 9(2): 167–76. - PubMed
-
- Iihara K, Nishimura K, Kada A, Nakagawara J, Ogasawara K, Ono J, Shiokawa Y, Aruga T, Miyachi S, Nagata I, Toyoda K, Matsuda S, Miyamoto Y, Suzuki A, Ishikawa KB, Kataoka H, Nakamura F, Kamitani S. Effects of comprehensive stroke care capabilities on in-hospital mortality of patients with ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke: J-aspect study. PLoS One 2014; 9(5): e96819. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

