Bioproduction, characterization, anticancer and antioxidant activities of extracellular melanin pigment produced by newly isolated microbial cell factories Streptomyces glaucescens NEAE-H
- PMID: 28195138
- PMCID: PMC5307326
- DOI: 10.1038/srep42129
Bioproduction, characterization, anticancer and antioxidant activities of extracellular melanin pigment produced by newly isolated microbial cell factories Streptomyces glaucescens NEAE-H
Abstract
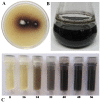
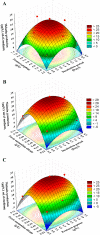
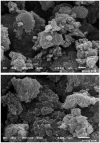
In this present study, a newly isolated strain, Streptomyces sp. NEAE-H, capable of producing high amount of black extracellular melanin pigment on peptone-yeast extract iron agar and identified as Streptomyces glaucescens NEAE-H. Plackett-Burman statistical design was conducted for initial screening of 17 independent (assigned) variables for their significances on melanin pigment production by Streptomyces glaucescens NEAE-H. The most significant factors affecting melanin production are incubation period, protease-peptone and ferric ammonium citrate. The levels of these significant variables and their interaction effects were optimized by using face-centered central composite design. The maximum melanin production (31.650 μg/0.1 ml) and tyrosinase activity (6089.10 U/ml) were achieved in the central point runs under the conditions of incubation period (6 days), protease-peptone (5 g/L) and ferric ammonium citrate (0.5 g/L). Melanin pigment was recovered by acid-treatment. Higher absorption of the purified melanin pigment was observed in the UV region at 250 nm. It appeared to have defined small spheres by scanning electron microscopy imaging. The maximum melanin yield was 350 mg dry wt/L of production medium. In vitro anticancer activity of melanin pigment was assayed against skin cancer cell line using MTT assay. The IC50 value was 16.34 ± 1.31 μg/ml for melanin and 8.8 ± 0.5 μg/ml for standard 5-fluorouracil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures





References
-
- Langfelder K., Streibel M., Jahn B., Haase G. & Brakhage A. A. Biosynthesis of fungal melanins and their importance for human pathogenic fungi. Fungal Genet Biol 38, 143–158 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Ikeda K. et al.. Construction of a new cloning vector utilizing a cryptic plasmid and the highly expressed melanin-synthesizing gene operon from Streptomyces castaneoglobisporus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 168, 195–199 (1998).
-
- Marino S. M. et al.. Investigation of Streptomyces antibioticus tyrosinase reactivity toward chlorophenols. Arch Biochem Biophys 505, 67–74 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Seetharam G. B. & Saville B. A. Degradation of phenol using tyrosinase immobilized on siliceous supports. Water Res 37, 436–440 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Tarangini K. & Mishra S. Production, characterization and analysis of melanin from isolated marine Pseudomonas sp. using vegetable waste. Res J Eng Sci 2(5), 40–46 ISSN 2278: 9472 (2013).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

