Rare damaging variants in DNA repair and cell cycle pathways are associated with hippocampal and cognitive dysfunction: a combined genetic imaging study in first-episode treatment-naive patients with schizophrenia
- PMID: 28195569
- PMCID: PMC5438026
- DOI: 10.1038/tp.2016.291
Rare damaging variants in DNA repair and cell cycle pathways are associated with hippocampal and cognitive dysfunction: a combined genetic imaging study in first-episode treatment-naive patients with schizophrenia
Abstract
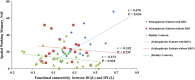
Schizophrenia is a complex neurodevelopmental disorder where changes in both hippocampus and memory-related cognitive functions are central. However, the exact relationship between neurodevelopmental-genetic factors and hippocampal-cognitive dysfunction remains unclear. The general aim of our study is to link the occurrence of rare damaging mutations involved in susceptibility gene pathways to the structure and function of hippocampus in order to define genetically and phenotypically based subgroups in schizophrenia. In the present study, by analyzing the exome sequencing and magnetic resonance imaging data in 94 first-episode treatment-naive schizophrenia patients and 134 normal controls, we identified that a cluster of rare damaging variants (RDVs) enriched in DNA repair and cell cycle pathways was present only in a subgroup including 39 schizophrenic patients. Furthermore, we found that schizophrenic patients with this RDVs show increased resting-state functional connectivity (rsFC) between left hippocampus (especially for left dentate gyrus) and left inferior parietal cortex, as well as decreased rsFC between left hippocampus and cerebellum. Moreover, abnormal rsFC was related to the deficits of spatial working memory (SWM; that is known to recruit the hippocampus) in patients with the RDVs. Taken together, our data demonstrate for the first time, to our knowledge, that damaging rare variants of genes in DNA repair and cell cycle pathways are associated with aberrant hippocampal rsFC, which was further relative to cognitive deficits in first-episode treatment-naive schizophrenia. Therefore, our data provide some evidence for the occurrence of phenotypic alterations in hippocampal and SWM function in a genetically defined subgroup of schizophrenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Tsuang MT, STONE WS, Faraone SV. Genes, environment and schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry 2001; 178: s18–s24. - PubMed
-
- Weinberger DR. Implications of normal brain development for the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1987; 44: 660–669. - PubMed
-
- Coryell W, Zimmerman M. The heritability of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder: a family study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1988; 45: 323–327. - PubMed
-
- Kendler KS, McGuire M, Gruenberg AM, O'Hare A, Spellman M, Walsh D. The Roscommon family study: I. Methods, diagnosis of probands, and risk of schizophrenia in relatives. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1993; 50: 527–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

