The Mole Mapper Study, mobile phone skin imaging and melanoma risk data collected using ResearchKit
- PMID: 28195576
- PMCID: PMC5308198
- DOI: 10.1038/sdata.2017.5
The Mole Mapper Study, mobile phone skin imaging and melanoma risk data collected using ResearchKit
Abstract
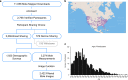
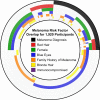
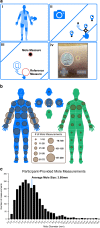
Sensor-embedded phones are an emerging facilitator for participant-driven research studies. Skin cancer research is particularly amenable to this approach, as phone cameras enable self-examination and documentation of mole abnormalities that may signal a progression towards melanoma. Aggregation and open sharing of this participant-collected data can be foundational for research and the development of early cancer detection tools. Here we describe data from Mole Mapper, an iPhone-based observational study built using the Apple ResearchKit framework. The Mole Mapper app was designed to collect participant-provided images and measurements of moles, together with demographic and behavioral information relating to melanoma risk. The study cohort includes 2,069 participants who contributed 1,920 demographic surveys, 3,274 mole measurements, and 2,422 curated mole images. Survey data recapitulates associations between melanoma and known demographic risks, with red hair as the most significant factor in this cohort. Participant-provided mole measurements indicate an average mole size of 3.95 mm. These data have been made available to engage researchers in a collaborative, multidisciplinary effort to better understand and prevent melanoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Dataset use reported in
- doi: 10.1038/nature11624
References
Data Citations
-
- Webster D. E. 2016. Synapse. http://dx.doi.org/10.7303/syn6829807.1 - DOI
-
- Webster D. E. 2016. Synapse. http://dx.doi.org/10.7303/syn6829810.1 - DOI
-
- Webster D. E. 2016. Synapse. http://dx.doi.org/10.7303/syn6829811.1 - DOI
-
- Webster D. E. 2016. Synapse. http://dx.doi.org/10.7303/syn6829808.1 - DOI
-
- Webster D. E. 2016. Synapse. http://dx.doi.org/10.7303/syn6829809.1 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

