Characterization of Human Cancer Cell Lines by Reverse-phase Protein Arrays
- PMID: 28196595
- PMCID: PMC5501076
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.01.005
Characterization of Human Cancer Cell Lines by Reverse-phase Protein Arrays
Abstract
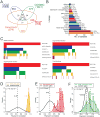
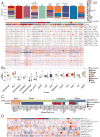
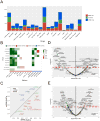
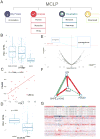
Cancer cell lines are major model systems for mechanistic investigation and drug development. However, protein expression data linked to high-quality DNA, RNA, and drug-screening data have not been available across a large number of cancer cell lines. Using reverse-phase protein arrays, we measured expression levels of ∼230 key cancer-related proteins in >650 independent cell lines, many of which have publically available genomic, transcriptomic, and drug-screening data. Our dataset recapitulates the effects of mutated pathways on protein expression observed in patient samples, and demonstrates that proteins and particularly phosphoproteins provide information for predicting drug sensitivity that is not available from the corresponding mRNAs. We also developed a user-friendly bioinformatic resource, MCLP, to help serve the biomedical research community.
Keywords: biomarker; cancer cell lines; data portal; drug sensitivity; proteomics; reverse-phase protein array; signaling pathways.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Byers LA, Diao L, Wang J, Saintigny P, Girard L, Peyton M, Shen L, Fan Y, Giri U, Tumula PK, et al. An epithelial-mesenchymal transition gene signature predicts resistance to EGFR and PI3K inhibitors and identifies Axl as a therapeutic target for overcoming EGFR inhibitor resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:279–290. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA217685/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG008100/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA210950/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA098258/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA168394/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA217842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA070907/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA175486/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA176284/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA143883/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA199461/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA209851/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

