Rho Kinase Inhibition with Fasudil in the SOD1G93A Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis-Symptomatic Treatment Potential after Disease Onset
- PMID: 28197100
- PMCID: PMC5281550
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00017
Rho Kinase Inhibition with Fasudil in the SOD1G93A Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis-Symptomatic Treatment Potential after Disease Onset
Abstract
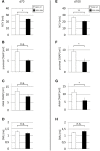
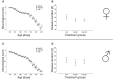
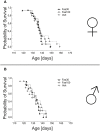
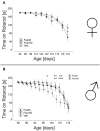
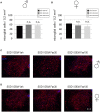
Despite an improved understanding of the genetic background and the pathomechanisms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) no novel disease-modifying therapies have been successfully implemented in clinical routine. Riluzole still remains the only clinically approved substance in human ALS treatment with limited efficacy. We have previously identified pharmacological rho kinase (ROCK) inhibitors as orally applicable substances in SOD1.G93A transgenic ALS mice (SOD1G93A), which are able to extend survival time and improve motor function after presymptomatic treatment. Here, we have evaluated the therapeutic effect of the orally administered ROCK inhibitor Fasudil starting at a symptomatic disease stage, more realistically reflecting the clinical situation. Oral Fasudil treatment was initiated at a symptomatic stage at 80 days of life (d80) with 30 or 100 mg/kg body weight in both female and male mice. While baseline neurological scoring and survival were not influenced, Fasudil significantly improved motor behavior in male mice. Spinal cord pathology of motoneurons (MN) and infiltrating microglial cells (MG) at disease end-stage were not significantly modified. Although treatment after symptom onset was less potent than treatment in asymptomatic animals, our study shows the therapeutic benefits of this well-tolerated substance, which is already in clinical use for other indications.
Keywords: Fasudil; ROCK; SOD1; mouse model of ALS; neuroprotection.
Figures


References
-
- Alves C. J., de Santana L. P., dos Santos A. J., de Oliveira G. P., Duobles T., Scorisa J. M., et al. . (2011). Early motor and electrophysiological changes in transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and gender differences on clinical outcome. Brain Res. 1394, 90–104. 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.02.060 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bermel C., Tonges L., Planchamp V., Gillardon F., Weishaupt J. H., Dietz G. P., et al. . (2009). Combined inhibition of Cdk5 and ROCK additively increase cell survival, but not the regenerative response in regenerating retinal ganglion cells. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 42, 427–437. 10.1016/j.mcn.2009.09.005 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

