Combining Smoothened Agonist and NEL-Like Protein-1 Enhances Bone Healing
- PMID: 28198775
- PMCID: PMC5443697
- DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000003367
Combining Smoothened Agonist and NEL-Like Protein-1 Enhances Bone Healing
Abstract
Background: Nonhealing bone defects represent an immense biomedical burden. Despite recent advances in protein-based bone regeneration, safety concerns over bone morphogenetic protein-2 have prompted the search for alternative factors. Previously, the authors examined the additive/synergistic effects of hedgehog and Nel-like protein-1 (NELL-1) on the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. In this study, the authors sought to leverage their previous findings by applying the combination of Smoothened agonist (SAG), hedgehog signal activator, and NELL-1 to an in vivo critical-size bone defect model.
Methods: A 4-mm parietal bone defect was created in mixed-gender CD-1 mice. Treatment groups included control (n = 6), SAG (n = 7), NELL-1 (n = 7), and SAG plus NELL-1 (n = 7). A custom fabricated poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) disk with hydroxyapatite coating was used as an osteoinductive scaffold.
Results: Results at 4 and 8 weeks showed increased bone formation by micro-computed tomographic analyses with either stimulus alone (SAG or NELL-1), but significantly greater bone formation with both components combined (SAG plus NELL-1). This included greater bone healing scores and increased bone volume and bone thickness. Histologic analyses confirmed a significant increase in new bone formation with the combination therapy SAG plus NELL-1, accompanied by increased defect vascularization.
Conclusions: In summary, the authors' results suggest that combining the hedgehog signaling agonist SAG and NELL-1 has potential as a novel therapeutic strategy for the healing of critical-size bone defects. Future directions will include optimization of dosage and delivery strategy for an SAG and NELL-1 combination product.
Figures
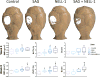

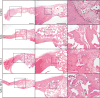
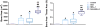
Comment in
-
Discussion: Combining Smoothened Agonist and NEL-Like Protein-1 Enhances Bone Healing.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017 Jun;139(6):1397-1398. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000003368. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017. PMID: 28538564 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Nell-1 Is a Key Functional Modulator in Osteochondrogenesis and Beyond.J Dent Res. 2019 Dec;98(13):1458-1468. doi: 10.1177/0022034519882000. Epub 2019 Oct 14. J Dent Res. 2019. PMID: 31610747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calvarial Defect Healing Induced by Small Molecule Smoothened Agonist.Tissue Eng Part A. 2016 Dec;22(23-24):1357-1366. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2016.0167. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016. PMID: 27702396 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Systemic Therapy of PEGylated NEL-Like Protein 1 (NELL-1) on Fracture Healing in Mice.Am J Pathol. 2018 Mar;188(3):715-727. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2017.11.018. Epub 2017 Dec 30. Am J Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29294300 Free PMC article.
-
Nell-1 enhances bone regeneration in a rat critical-sized femoral segmental defect model.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011 Feb;127(2):580-587. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181fed5ae. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2011. PMID: 21285762 Free PMC article.
-
The role of NELL-1, a growth factor associated with craniosynostosis, in promoting bone regeneration.J Dent Res. 2010 Sep;89(9):865-78. doi: 10.1177/0022034510376401. Epub 2010 Jul 20. J Dent Res. 2010. PMID: 20647499 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nell-1 Is a Key Functional Modulator in Osteochondrogenesis and Beyond.J Dent Res. 2019 Dec;98(13):1458-1468. doi: 10.1177/0022034519882000. Epub 2019 Oct 14. J Dent Res. 2019. PMID: 31610747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NELL-1 Increased the Osteogenic Differentiation and mRNA Expression of Spheroids Composed of Stem Cells.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Jun 8;57(6):586. doi: 10.3390/medicina57060586. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 34201046 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Activation for Craniofacial Bone Regeneration in a Critical-Sized Rat Mandibular Defect.JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2019 Mar 1;21(2):110-117. doi: 10.1001/jamafacial.2018.1508. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2019. PMID: 30520953 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Hedgehog signaling Offers A Novel Perspective for Bone Homeostasis Disorder Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 16;20(16):3981. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163981. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31426273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circadian BMAL1 regulates mandibular condyle development by hedgehog pathway.Cell Prolif. 2020 Jan;53(1):e12727. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12727. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 31747713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nandi SK, Roy S, Mukherjee P, Kundu B, De DK, Basu D. Orthopaedic applications of bone graft & graft substitutes: a review. Indian J Med Res. 2010;132:15–30. - PubMed
-
- Giannoudis PV, Dinopoulos H, Tsiridis E. Bone substitutes: an update. Injury. 2005;36(Suppl 3):S20–27. - PubMed
-
- Silber JS, Anderson DG, Daffner SD, et al. Donor site morbidity after anterior iliac crest bone harvest for single-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. Spine. 2003;28:134–139. - PubMed
-
- Younger EM, Chapman MW. Morbidity at bone graft donor sites. Journal of orthopaedic trauma. 1989;3:192–195. - PubMed
-
- Ahlmann E, Patzakis M, Roidis N, Shepherd L, Holtom P. Comparison of anterior and posterior iliac crest bone grafts in terms of harvest-site morbidity and functional outcomes. The Journal of bone and joint surgery American volume. 2002;84-a:716–720. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

