Effect of two desensitizing agents on dentin permeability in vitro
- PMID: 28198974
- PMCID: PMC5289398
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-77572016-0228
Effect of two desensitizing agents on dentin permeability in vitro
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this in vitro study was to investigate the effect of two desensitizing agents and water on hydraulic conductance in human dentin.
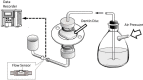
Material and methods: GLUMA Desensitizer PowerGel (GLU) contains glutaraldehyde (GA) and 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA), and Teethmate Desensitizer (TD) is a powder comprising tetracalcium phosphate (TTCP) and dicalcium phosphate anhydrous (DCPA) that is mixed with water. Deionized water was used as a negative control (CTR). Thirty discs with a thickness of 1.2 mm were cut from the coronal dentin of the third molars and cleaned with 0.5 M EDTA (pH 7.4). After being mounted in a split-chamber device, the discs were pressurized with water at 1 kPa and 3 kPa in order to measure flow rates with a highly sensitive micro-flow sensor and to calculate hydraulic conductance as a baseline value (BL). Following the application of GLU, TD, and CTR (n=10), hydraulic conductance was remeasured with intermittent storage in water after 15 min, 1 d, 1 w, and 1 m. Reduction in permeability (PR%) was calculated from hydraulic conductance. Data were statistically analyzed using nonparametric methods (α<0.05). Representative discs were inspected by SEM.
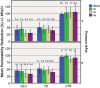
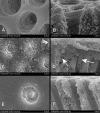
Results: PR% for GLU and TD were 30-50% 15 min and 1 m after their application. Post hoc tests indicated that PR% of CTR was significantly greater than those of GLU and TD at all time points tested. The PR% of GLU and TD were not significantly different. SEM examinations showed noncollapsed collagen meshes at the tubular entrances after GLU, and crystalline precipitates occluding the tubular orifices after TD, whereas CTR specimens showed typical patterns of etched dentin.
Conclusions: The present study on hydraulic conductance in dentin discs treated with two chemically different desensitizing agents and water as a control demonstrated that both products may be characterized as effective.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vitro dentin permeability after application of Gluma® desensitizer as aqueous solution or aqueous fumed silica dispersion.J Appl Oral Sci. 2011 Apr;19(2):147-53. doi: 10.1590/s1678-77572011000200011. J Appl Oral Sci. 2011. PMID: 21552716 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of desensitizing agents on human dentin permeability.Am J Dent. 1998 Dec;11(6):286-90. Am J Dent. 1998. PMID: 10477980
-
In vitro evaluation of dentinal hydraulic conductance and tubule sealing by a novel calcium-phosphate desensitizer.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013 Feb;101(2):303-9. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.32840. Epub 2012 Nov 19. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013. PMID: 23166091
-
Effect of dentin desensitizers and dentin bonding agents on dentin permeability.Am J Dent. 2000 Feb;13(1):21-7. Am J Dent. 2000. PMID: 11763898
-
Effectiveness and acid/tooth brushing resistance of in-office desensitizing treatments-A hydraulic conductance study.Arch Oral Biol. 2018 Dec;96:130-136. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2018.09.004. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Arch Oral Biol. 2018. PMID: 30237094
Cited by
-
A novel treatment based on powder jet deposition technique for dentin hypersensitivity: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Sep 27;23(1):695. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03431-y. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37759198 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
S-PRG-based toothpastes compared to NaF toothpaste and NaF varnish on dentin permeability in vitro.J Appl Oral Sci. 2022 Jun 6;30:e20220082. doi: 10.1590/1678-7757-2022-0082. eCollection 2022. J Appl Oral Sci. 2022. PMID: 35674543 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Study of Technologies for Tubule Occlusion and Treatment of Dentin Hypersensitivity.J Funct Biomater. 2021 Apr 27;12(2):27. doi: 10.3390/jfb12020027. J Funct Biomater. 2021. PMID: 33925548 Free PMC article.
-
Positive influence of simvastatin used as adjuvant agent for cavity lining.Clin Oral Investig. 2019 Sep;23(9):3457-3469. doi: 10.1007/s00784-018-2757-7. Epub 2018 Dec 14. Clin Oral Investig. 2019. PMID: 30552591
-
Effectiveness and cytotoxicity of two desensitizing agents: a dentin permeability measurement and dentin barrier testing in vitro study.BMC Oral Health. 2022 Sep 10;22(1):391. doi: 10.1186/s12903-022-02424-7. BMC Oral Health. 2022. PMID: 36088323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brännström M, Åström A. A study on the mechanism on pain elicited from the dentin. J Dent Res. 1964;43:619–625. - PubMed
-
- Camps J, Giustiniani S, Dejou J, Franquin JC. Low versus high pressure for in vitro determination of hydraulic conductance of human dentine. Arch Oral Biol. 1997;42:293–298. - PubMed
-
- Canadian Advisory Board on Dentin Hypersensitivity Consensus-based recommendations for the diagnosis and management of dentin hypersensitivity. J Can Dent Assoc. 2003;69:221–226. - PubMed
-
- Chabansky MB, Gillam DG. Aetiology, prevalence and clinical features of cervical dentine sensitivity. J Oral Rehabil. 1997;24:15–19. - PubMed
-
- Ciucchi B, Bouillaguet S, Holz J, Pashley DH. Dentinal fluid dynamics in human teeth, in vivo. J Endodon. 1995;21:191–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

