Adipose-derived circulating miRNAs regulate gene expression in other tissues
- PMID: 28199304
- PMCID: PMC5330251
- DOI: 10.1038/nature21365
Adipose-derived circulating miRNAs regulate gene expression in other tissues
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Adipose-derived circulating miRNAs regulate gene expression in other tissues.Nature. 2017 May 10;545(7653):252. doi: 10.1038/nature22319. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28492253 No abstract available.
Abstract
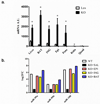
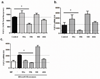
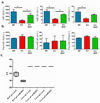
Adipose tissue is a major site of energy storage and has a role in the regulation of metabolism through the release of adipokines. Here we show that mice with an adipose-tissue-specific knockout of the microRNA (miRNA)-processing enzyme Dicer (ADicerKO), as well as humans with lipodystrophy, exhibit a substantial decrease in levels of circulating exosomal miRNAs. Transplantation of both white and brown adipose tissue-brown especially-into ADicerKO mice restores the level of numerous circulating miRNAs that are associated with an improvement in glucose tolerance and a reduction in hepatic Fgf21 mRNA and circulating FGF21. This gene regulation can be mimicked by the administration of normal, but not ADicerKO, serum exosomes. Expression of a human-specific miRNA in the brown adipose tissue of one mouse in vivo can also regulate its 3' UTR reporter in the liver of another mouse through serum exosomal transfer. Thus, adipose tissue constitutes an important source of circulating exosomal miRNAs, which can regulate gene expression in distant tissues and thereby serve as a previously undescribed form of adipokine.
Figures
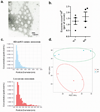
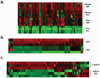
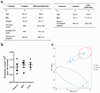
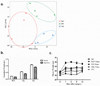
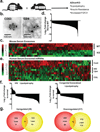
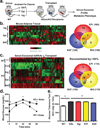
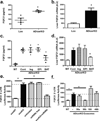
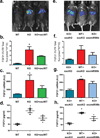
Comment in
-
Adipose tissue: Exosomal microRNAs - novel adipokines.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017 Apr;13(4):188. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.22. Epub 2017 Feb 24. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28232665 No abstract available.
-
Non-coding RNA: Exosomal microRNAs as novel adipokines.Nat Rev Genet. 2017 Apr;18(4):212. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2017.14. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Nat Rev Genet. 2017. PMID: 28239157 No abstract available.
-
Brown Fat-Derived Exosomes: Small Vesicles with Big Impact.Cell Metab. 2017 Apr 4;25(4):759-760. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.03.012. Cell Metab. 2017. PMID: 28380368
-
The Micro-Managing Fat: Exosomes as a New Messenger.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Aug;28(8):541-542. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2017.04.004. Epub 2017 May 10. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28501497 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose-derived exosomal MicroRNAs orchestrate gene regulation in the liver: Is this the missing link in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease?Hepatology. 2017 Nov;66(5):1689-1691. doi: 10.1002/hep.29343. Epub 2017 Sep 29. Hepatology. 2017. PMID: 28653754 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

