Modulation of cholesterol transport by maternal hypercholesterolemia in human full-term placenta
- PMID: 28199412
- PMCID: PMC5310867
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171934
Modulation of cholesterol transport by maternal hypercholesterolemia in human full-term placenta
Abstract
The significance of maternal cholesterol transporting to the fetus under normal as well as pathological circumstances is less understood. The objective of this study was to observe the effects of maternal hypercholesterolemia on placental cholesterol transportation. Human full-time placenta, maternal and venous cord blood were sampled at delivery from the pregnant women with serum total cholesterol (TC) concentrations at third trimester higher than 7.25 mM (n = 19) and the pregnant women with normal TC concentrations (n = 19). Serum lipids and expression of genes related to cholesterol transportation were measured by western blot or real-time PCR. The results indicated that serum TC, high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels were significantly increased, in pregnancies, but decreased in cord blood in hypercholesterolemic group compared to the matched control group. All the subjects were no-drinking, non-smoker, and gestational disease free. The mRNA expression of lipoprotein receptors, including LDLR and VLDLR were significantly increased, while the protein expression of PCSK9 was significantly increased in hypercholesterolemic placenta. In conclusion, maternal hypercholesterolemia might decrease the transportation of cholesterol from mother to fetus because of the high levels of PCSK9 protein expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

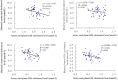
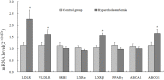

References
-
- Piechota W, Staszewski A. Reference ranges of lipids and apolipoproteins in pregnancy. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1992; 16;45(1):27–35. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

