The Survival of Motor Neuron Protein Acts as a Molecular Chaperone for mRNP Assembly
- PMID: 28199839
- PMCID: PMC5492976
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.01.059
The Survival of Motor Neuron Protein Acts as a Molecular Chaperone for mRNP Assembly
Abstract
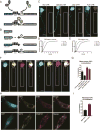
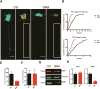
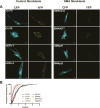
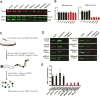
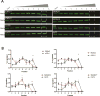
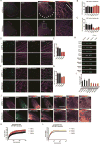
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a motor neuron disease caused by reduced levels of the survival of motor neuron (SMN) protein. SMN is part of a multiprotein complex that facilitates the assembly of spliceosomal small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs). SMN has also been found to associate with mRNA-binding proteins, but the nature of this association was unknown. Here, we have employed a combination of biochemical and advanced imaging methods to demonstrate that SMN promotes the molecular interaction between IMP1 protein and the 3' UTR zipcode region of β-actin mRNA, leading to assembly of messenger ribonucleoprotein (mRNP) complexes that associate with the cytoskeleton to facilitate trafficking. We have identified defects in mRNP assembly in cells and tissues from SMA disease models and patients that depend on the SMN Tudor domain and explain the observed deficiency in mRNA localization and local translation, providing insight into SMA pathogenesis as a ribonucleoprotein (RNP)-assembly disorder.
Keywords: IMP1; SMA; SMN; beta actin mRNA; mRNA localization; mRNP; spinal muscular atrophy.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Buhler D, Raker V, Luhrmann R, Fischer U. Essential role for the tudor domain of SMN in spliceosomal U snRNP assembly: implications for spinal muscular atrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 1999;8:2351–2357. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

